LZT 123 1836
38
During microprocessor supervised mode, the GS64 takes a current-limited voltage
source at the CHG_IN pin to implement constant-current charging of a single Li-Ion
cell connected to the VCC pins.
BATTERY
CHARGER
CONTROL
BATTERY
CHARGER
CONTROL
TIMER
TIMER
+
-
3.6V
50mA
3.6V
50mA
MAX CURRENT
DETECTION
ADC
SUI
SUI
TO
uPC
V
REF1
ADIN1
C1
V
REF2
VCC
SINGLE
CELL Li-ION
VOLTAGE
SOURCE
CHG_IN
D1
CHARGE FET
+
-
BATTERY
CHARGER
CONTROL
BATTERY
CHARGER
CONTROL
TIMER
TIMER
+
-
3.6V
50mA
3.6V
50mA
MAX CURRENT
DETECTION
ADC
SUI
SUI
TO
uPC
V
REF1
V
REF1
ADIN1
C1
V
REF2
V
REF2
VCC
SINGLE
CELL Li-ION
VOLTAGE
SOURCE
CHG_IN
D1
CHARGE FET
+
-
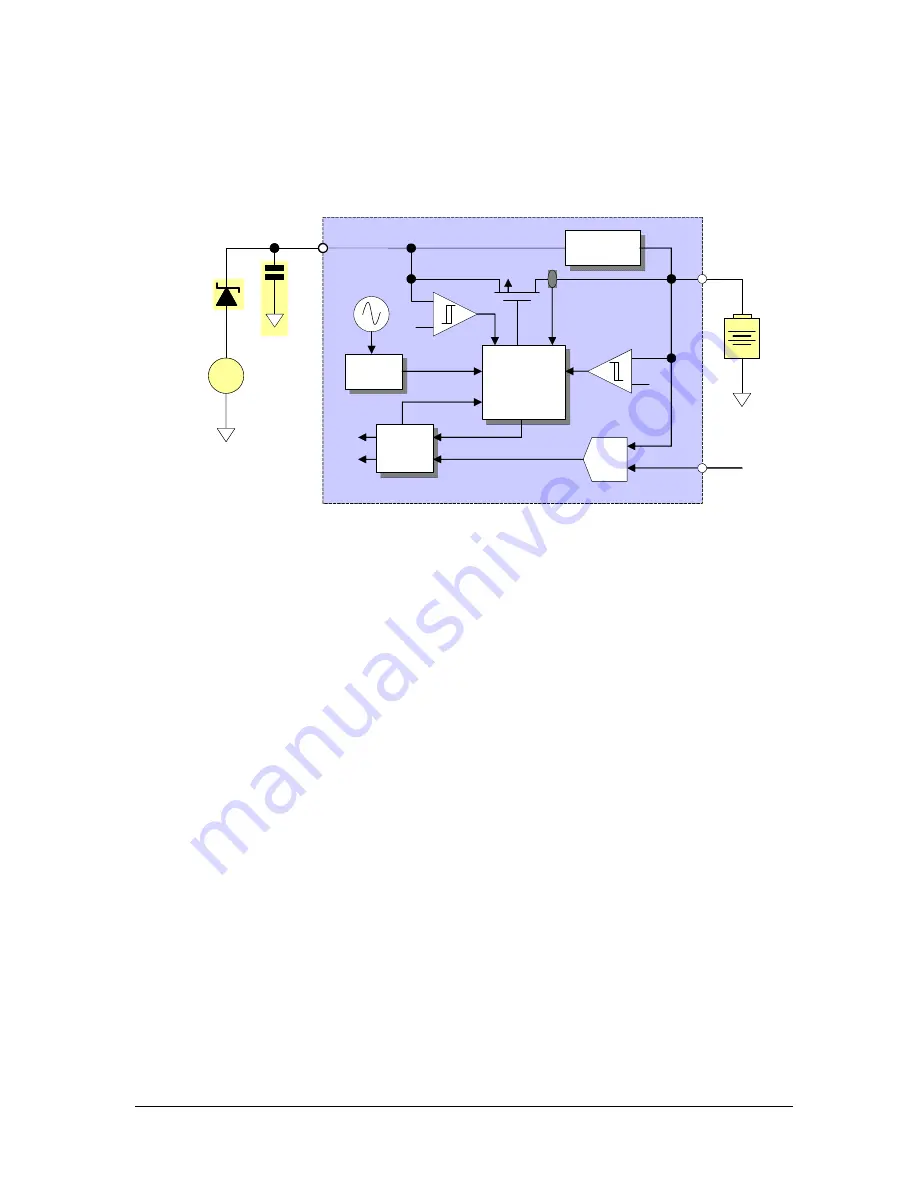
Figure 5.7-1 Typical application for pulse charging a battery
5.7.1
Charging Process
Figure 5.7-1 shows a typical battery charging implementation. The voltage source
must be current limited (500 mA max). A reverse current protection diode prevents
external fault conditions from draining the battery. A small (typ 10
µ
F) capacitor
should be placed close to the CHG_IN pin.
In the application shown, a conditioning phase slowly raises the voltage of a deeply
discharged cell to a level suitable for fast-charging. After cell conditioning is
complete, the microprocessor uses the GS64’S ADC converter to monitor the battery
cell’s status and uses the power management block to control the charge-FET.
A charge request is initiated when an external voltage source is applied to the
CHG_IN pin. However, before this request is passed to the microprocessor, CHG_IN is
verified to be greater than VCC by 150 mV, and at least 3.7 V. If the latter criteria is
not met, the module limits charging to the conditioning phase. If the former criteria
is not met, the charge request is ignored and all charging is disabled. If the CHG_IN
voltage exceeds the upper limit of 6.3 V it will be detected by the module, but
charging is not inhibited. In this case, however, CHG_IN is outside the normal
operating range of the device, so the software will not initiate charging if CHG_IN >
6.3 V is detected.
















































