MSK500/1
+MB500/1+MR500
Datum 12.05.2015
Art.Nr. 81413
Änd. Stand 87/15
11
viewing side = plug-in side
plug pin
Fig. 10: Determination of the pole position. Cutting
the magnetic strip
Fig. 11: Determination of the pole position. Joining
the magnetic strip
Signal
inverted
inverted with
reference signal
A
Pin 1
Pin 1
B
2
2
I, R
- - -
3
+UB
4
4
GND
5
5
A/
6
6
B/
7
7
I/, R/
- - -
8
nc
3, 8, 9
9
E8E:
Connection with 9 pole D-SUB plug.
Signal inverted with
reference
signal
nc
PIN 1
I/, R/
2
B/
3
A
4
GND
5
+UB
6
I, R
7
B
8
A/
9
5. Joining magnetic strips together
For some applications it may be necessary to extend
the magnetic strip. The magnetic strip can be cut
and rejoined using standard tools.
But however carefully this is done the accuracy of
the strip at the join will be impaired (error of at
least 0.1 ... 0.2 mm).
The following tools / accessories are required:
• magnet magnifier, magnetic foil or metal dust
• rule or suitable tool
• compass needle
Steps
• If there is a cover strip, this is to be removed first.
• To determine the pole division either use metal
dust, a magnet magnifier or magnetic foil.
• If necessary, use a compass needle to determine the
location of the poles on the magnetic strip (fig. 10).
• Use a rule and a sharp knife to cut the magnetic
strip at a right angle. Then also cut the carrier
strip accordingly.
• Previous steps are to be repeated with the other
part of strip.
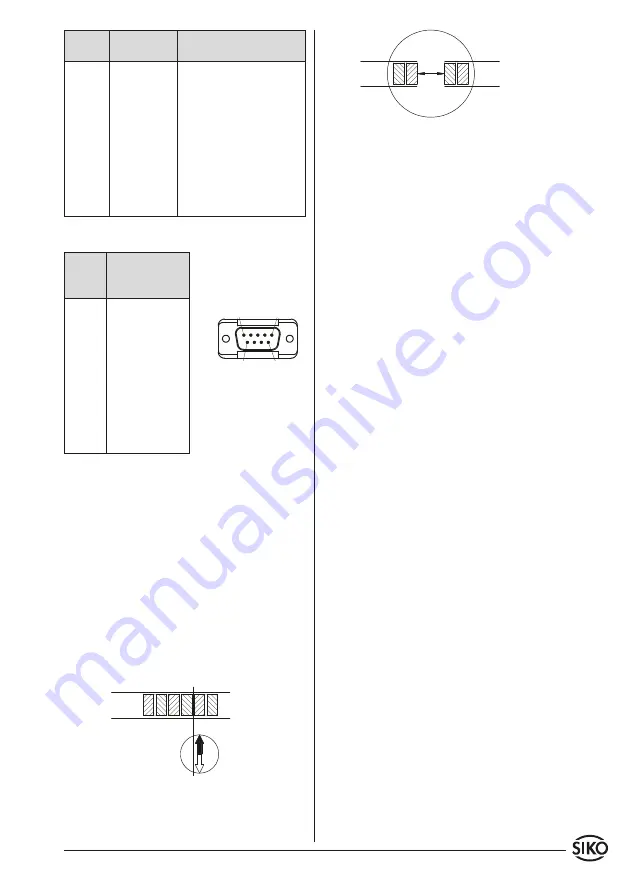
• Check polarity before joining the two parts.
Both ends must attract each other (if necessary,
use compass needle). In case both ends have the
same polarity, shorten one end by a half pole
division (fig. 11).
• Join the two ends closely together and add the
cover strip.
6. Maintenance
We recommend cleaning the magnetic strip's sur-
face from time to time with a soft rag. This avoids
dirt (dust, chips, humidity ...) sticking to the strip.
7. Trouble shooting
Below are some typical errors which may occur duri-
ng installation and operation:
• Magnetic strip incorrectly mounted (active sur-
face must be mounted towards the sensor) (see
chapter 3.1).
• Use of foreign protective strip. Must always be
non-magnetic.
• Sensor not or incorrectly connected (pin connec-
tion, see chapter 4.2).
• Tolerance for the gap between magnetic sensor
and magnetic strip not observed over the
total
travel distance. Sensor touches strip (see fig. 6+7).
• Cable squeezed / interrupted / cut by sharp edges.
• Sensor's active side not mounted towards the
magnetic strip (see fig. 6+7).
• Sensor has not been aligned according to fig. 6+7.












