System configuration and system status (web interface)
6.4 Powerline
Power Line Booster
Operating Instructions, 11/2019, A5E36203125A-AG
111
6.4.4.5
Signal-to-noise ratio
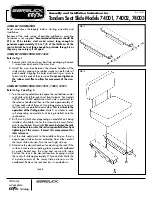
Figure 6-24 Signal-to-noise ratio
The signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) measures the quality of the powerline useful signal that is
covered by noise.
You can find a general explanation of operating this metering function under Signal graphs
(Page 108).
To extract the user data safely from the powerline signal, the useful signal must stand out
from the background noise. This means the signal-to-noise ratio must be sufficiently large. If
the SNR drops, the error rate increases and the modulation of the respective carrier is
reduced which is then also reflected in the Tone Map (Page 109). For a relatively good
signal-to-noise ratio, the transmit level set under Signal configuration (Page 110) should be
as high as possible. If the SNR is poor, the background noise can be determined by a PSD
measurement (Page 110) to identify potential interferences (e.g. by frequency converters or
incorrectly applied shielding). The comparison of two neighboring vehicles can indicate
whether the entire segment or only one station is affected.
Summary of Contents for SIMATIC Power Line Booster
Page 34: ......