8.3
User Memory Organization in the CPU 948
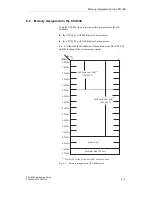
Depending on the version of the CPU 948 used, the user memory
occupies the memory area from 0 0000H to C FFFFH. When you
load the individual blocks of your program, they are stored in the
memory in random order (with addresses in ascending order).
Block management
When you correct a block, the old block in the memory is declared
invalid (i.e., the start ID is overwritten) and a new block is entered in
the memory and the address list. This also applies when you delete
blocks. The blocks are not really deleted in the memory but simply
declared invalid. Gaps created by deleting are managed as available
memory locations and are used again when you load new blocks.
Compressing memory
The online COMPRESS MEMORY PG function pushes all valid
blocks in the memory together. When you activate the COMPRESS
MEMORY while the CPU is in the STOP mode, all blocks that are not
directly next to each other are shifted. However, when you activate
this function while the CPU is in the RUN mode, long data and
extended data blocks (i.e., longer than 512 data words) are not shifted
because of data length consistency. Compressing produces large
available memory areas which you can use for loading new blocks.
If the online COMPRESS MEMORY PG function is interrupted (e.g.,
when the power is turned off), compressing is terminated and does not
resume automatically when power is turned on.
Location of blocks in the
user memory
In the CPU 948, blocks are stored so that data word DW 0 or the first
STEP 5 statement of each block is located at a paragraph address.
Paragraph addresses are at 16-word boundaries. Therefore, all blocks
begin in the memory at the address xxxxBH (bit no. 0 to 3 = BH) and
all block bodies at the address yyyy0H (bit no. 0 to 3 = 0H). The gaps
that result between blocks are filled in by invalid data blocks, so that
all blocks continue to exist in consecutive order.
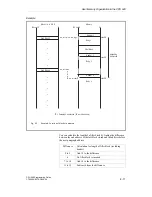
Filler blocks
These invalid data blocks are known as "filler blocks". They are
treated in the same way as the other blocks by the memory
management and have the following structure:
Start ID:
7070H
;
Block type/block number:
01FBH
;DB 251 invalid
Programmer ID:
00FFH
;irrelevant
Library number:
FFFFH
;irrelevant
Block length:
00XXH
;length 5 to 20 words
Data:
FFFFH
;according
:
;to
:
;length;
FFFFH
;can be left out entirely
User Memory Organization in the CPU 948
CPU 948 Programming Guide
8 - 10
C79000-G8576-C848-04
Summary of Contents for CPU 948
Page 10: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 1 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 32: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 2 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 72: ...Data Blocks CPU 948 Programming Guide 2 42 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 74: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 3 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 154: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 4 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 200: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 5 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 308: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 7 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 324: ...Examples of Parameter Assignment CPU 948 Programming Guide 7 18 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 326: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 8 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 370: ...Addressable System Data Area CPU 948 Programming Guide 8 46 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 372: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 9 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 486: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 11 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 522: ...PG Functions via the S5 Bus CPU 948 Programming Guide 11 38 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 524: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 12 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 538: ...Contents CPU 948 Programming Guide 13 2 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...
Page 546: ...List of Key Words CPU 948 Programming Guide Index 6 C79000 G8576 C848 04 ...