ADM-880C 07/20/09
38
7.0 PRESSURE MEASUREMENT
7.1 DIFFERENTIAL PRESSURE
Differential pressure measurements can be made with static pressure probes, a pitot tube or by connecting the pneumatic
tubing directly to any appropriate pressure source
within the safe operating limits for the meter
. The manner in which
a pitot tube is connected to the meter is critical to the type of differential pressure measurement obtained. The meter will
display DIFF PRES and read out in the same units for all types of differential pressure measurements.
The positive (+) and negative (-) ports of the meter are connected as a pair to the pneumatic pressure source for differential
pressure measurements. Maximum safe pressures for differential pressure measurements are 20 psid (900% full scale)
and 60 psia common mode. The length of each external pneumatic tube should not exceed 18 feet of 3/16" ID tubing.
Press the MODE key to toggle through the modes to differential pressure. The meter will display [DIFF PRES] and then
[IN READ]. Press the READ key to obtain the pressure measurement.
The differential pressure between two rooms, or any other two areas may be obtained by connecting the tubing to the
positive (+) port of the meter and leaving the negative (-) port open to the ambient air pressure. Place the end of the tubing
in one area and place the meter in the other. The meter will measure the pressure differential between the two areas.
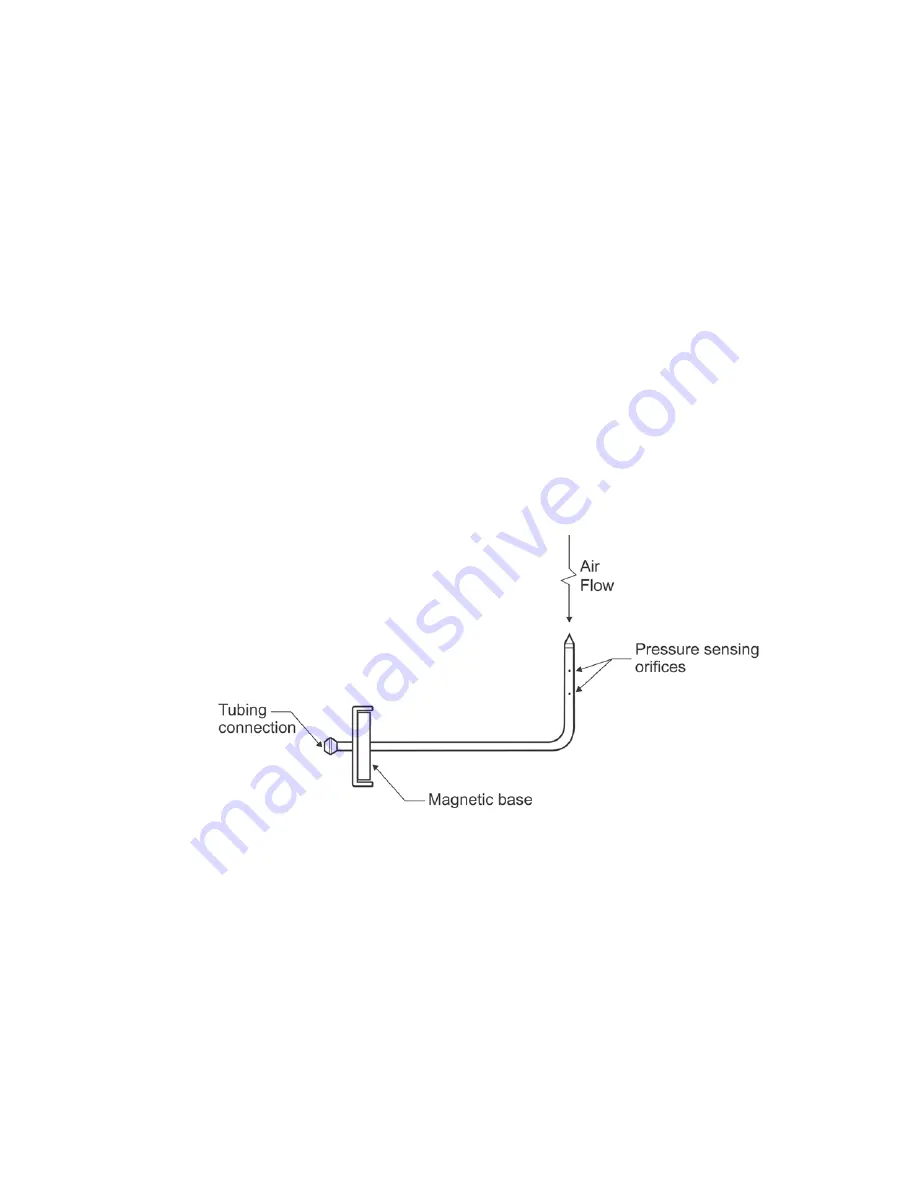
7.1.1 STATIC PRESSURE PROBES
Static pressures are measured with static pressure probes. These probes are brass colored and have a single tubing
connection in the magnetic base. Connect the tubing from the static pressure probe to the positive (+) port of the meter.
Leave the negative (-) port open to the room air. Insert the static pressure probe into a 3/8" hole drilled into the duct until
the magnet is flush with the surface of the duct. Point the tip of the static pressure probe directly into the airstream. Press
the READ key. The meter will read the differential between the pressure within the duct and the ambient pressure on the
negative port of the meter.
7.1 STATIC PRESSURE PROBE
7.1.2 PITOT TUBE "VELOCITY PRESSURES"
Velocity pressures are obtained when a pitot tube is used and the meter is set to read out in differential pressure. The
resulting reading is recorded as velocity pressure. Connect one of the tubing sections from the positive (+) port of the meter
to the total pressure connection (in line with the main shaft) on the pitot tube and connect the negative (-) port to the static
pressure connection (perpendicular to the main shaft). The pitot tube connections are shown in Figure 6.1. If the
connections are reversed, the readings will be negative. Insert the pitot tube into a 3/8" hole drilled into the side of the duct,
being careful to align the point of the pitot tube so that it is facing directly into the airstream. If the negative (-) connection
(perpendicular to the main shaft) of the pitot tube is upstream and parallel to the duct, the point of the pitot tube should be
facing directly into the airstream.
7.1.3 PITOT TUBE "STATIC PRESSURES"
Static pressures may be obtained using the pitot tube and the differential pressure mode by connecting the positive (+) port
on the meter to the static pressure connection (perpendicular to the main shaft) of the pitot tube and leaving the negative
(-) port exposed to the ambient pressure. Insert the pitot tube into the airstream as discussed under Section 7.1.2 PITOT
TUBE VELOCITY PRESSURES above. The resulting pressure differential is recorded as static pressure.
Summary of Contents for AIRDATA ADM-880C
Page 42: ...ADM 880C 07 20 09 37 FIGURE 6 3 VELGRID ASSEMBLY...
Page 50: ...ADM 880C 07 20 09 45 FIGURE 10 1 FRAME STORAGE FIGURE 10 2 FLOWHOOD IN CASE...
Page 51: ...ADM 880C 07 20 09 46 FIGURE 10 3 FLOWHOOD ASSEMBLY...
Page 53: ...ADM 880C 07 20 09 48 FIGURE 10 7 1X5 FRAME ASSEMBLY FIGURE 10 8 3X3 FRAME ASSEMBLY...
















































