47
Appendix
• Background colours can subconsciously affect the
audience:
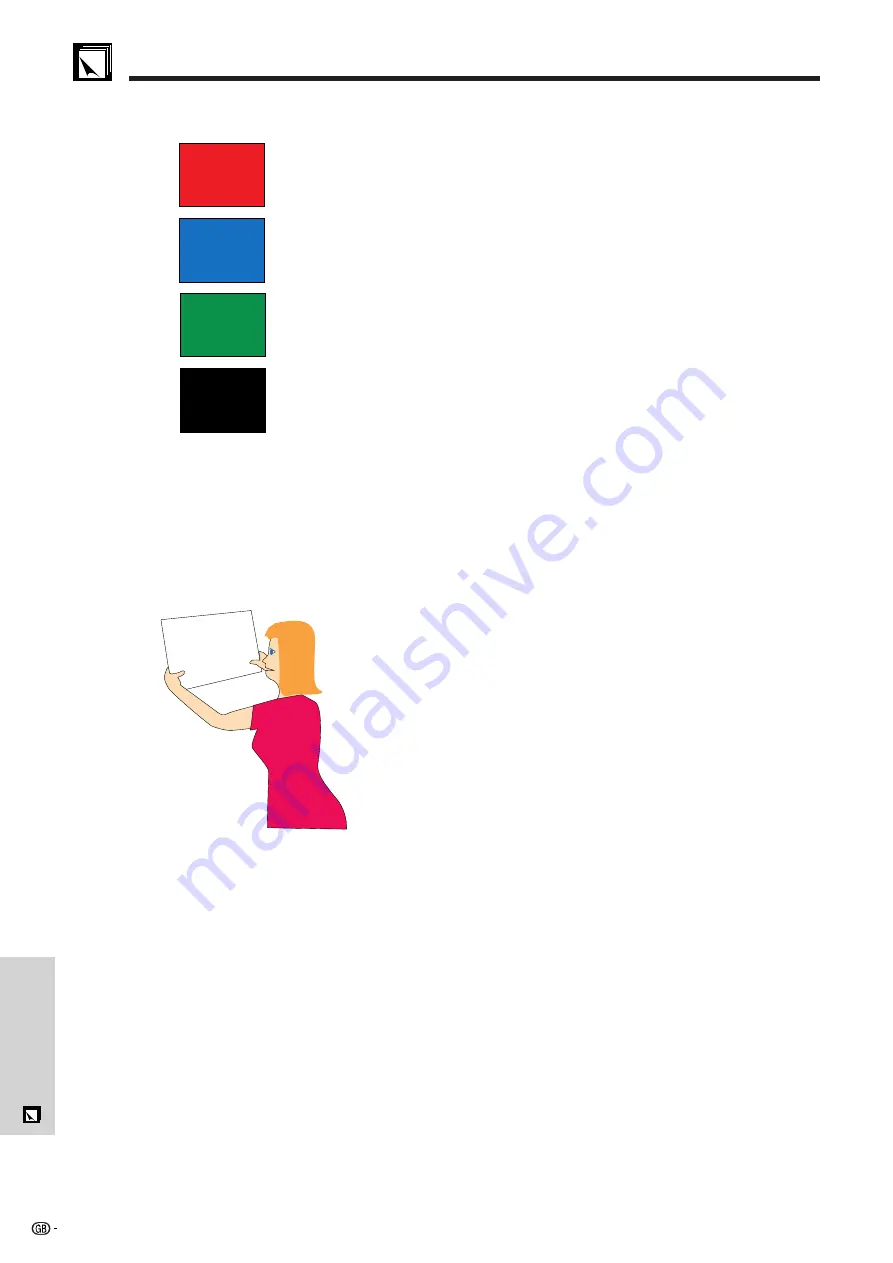
Red
—increases viewers’ pulse and breathing and
encourages risk taking but can also be associated with
financial loss.
Blue
—has a calming and conservative affect on the
audience but can also create boredom among corporate
audiences that are often inundated with this background
colour.
Green
—stimulates interaction.
Black
—conveys finality and certainty. Use it as a transitional
colour between slides when moving from one idea to
another.
• Foreground colours create a major impact on how well an
audience understands and remembers a message.
• Use one or two bright colours for emphasis.
• Highlight important messages.
• The eye has a difficult time reading certain coloured text on
certain coloured backgrounds. For example, text and
background colours in red and green, and blue and black
make for difficult viewing.
• Colourblind individuals may find it difficult to distinguish
between red and green, brown and green, and purple and
blue. Avoid using these colours together.
Fonts
• One of the most common mistakes in any type of
presentation visual is the selection of type fonts that are too
small, too thin, or too difficult to read.
• If you are not sure how well a given font will read on a screen
at various sizes, try this: Draw a 15 cm
20 cm box on a
piece of paper and print out several lines of text inside the
box with your computer printer at 300 or 600 dpi resolution.
Vary the sizes of text to simulate headline, body and text
call-outs for any charts or graphs. Hold the printout at arm’s
length. This is how your text will look on a 1.2 meters-wide
screen at 3 meters, on a 2.3 meters-wide screen at 6.1
meters and a 3.7 meters-wide screen at 9.1 meters. If you
cannot read the text easily, you should put less copy on
your visuals or use larger typefaces.
• Design your visuals so that they are visible by the viewer in
the last row.
• Nothing will ruin your presentation faster than misspelled
words. Take the time to proofread and edit your work before
your visuals become a permanent part of your presentation.
• Mixed case text is easier to read than text which is displayed
in capital letters.
• Another important attribute of fonts is whether any particular
face is serif or sans-serif. Serifs are small, usually horizontal
cross strokes that are added to the end of a letter’s main
strokes. Because of their ability to coax the eye along the
line of type, fonts with serifs are generally acknowledged to
be more readable.
Guide to Effective Presentations
Red
Blue
Green
Black
Presentation from SHARP
One of the most common mistakes in any type of
presentation visual is the selection of type fonts
that are too small, too thin, or hard to read.
Sans-serif
Serif






































