10
To measure the belt mass precisely, we recommend that you weigh the drive belt
and then recalculate this weight based on a belt length of 1 meter.
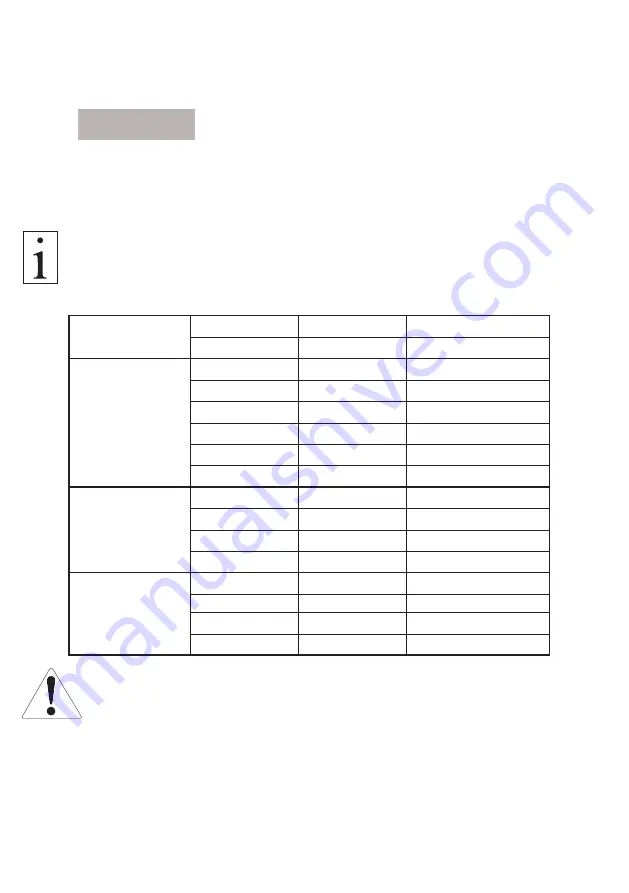
Ribbed V-belts
PJ = 0.082
PL = 0.320
PM = 1.100
kg/m per 10 ribs
V-belts
SPZ = 0.074
SPA = 0.123
SPB = 0.195
SPC = 0.377
kg/m per belt
10 = 0.064
13 = 0.109
17 = 0.196
20 = 0.266
22 = 0.324
25 = 0.420
32 = 0.668
40 = 0.958
kg/m per belt
Power belts
SPZ = 0.120
SPA = 0.166
SPB = 0.261
SPC = 0.555
kg/m per rib
3V/9J = 0.120
5V/15J = 0.252
8V/25J = 0.693
kg/m per rib
Polyurethane
T 2.5 = 0.015
T 5 = 0.024
toothed belts
T 10 = 0.048
T 20 = 0.084
kg/m per 10 mm width
AT 3 = 0.23
AT 5 = 0.034
AT 10 = 0.063
AT 20 = 0.106
kg/m per 10 mm width
Measurement deviations of up to +/- 10% for several measurements taken on
the same drive belt are as a rule not caused by a measurement error or fault
in the unit. In most cases, measurement deviations are due to the mechanical
tolerances of the drive systems.
Recommendation: Repeat the measuring 3 - 5 times and use the average as
measuring value.
Attention!
Newton or pound-force calculations have a
SQUARE factor higher error result!
The following table lists some examples of standard belt sizes:
3.5.2 Calculating the Strand Force in N / Lbf
To calculate the strand force, enter the belt mass and belt length with the membrane
keypad as described in Chapter 3.4. The strand force calculated is compared with the
set point value defined when the drive was designed.
The belt tension meter calculates the strand force using the formula:
F = 4
x
m
x
L
2
x
f
2
Where:
F = strand force in N
m = linear belt mass in kg/m
L = length of the free belt strand in m
f = natural frequency of the free belt measured in Hz






























