Seat Belts
14
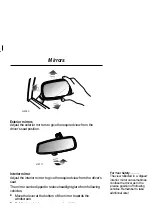
Caring for seat belts
Regularly inspect the belt webbing for signs of fraying, cuts and
wear, also pay particular attention to the condition of the fixing
points and adjusters.
Avoid contaminating the webbing with polish, oil and chemicals
(see ’Cleaning & car care’).
Three tests for checking seat belts
1. With the seat belt fastened, give the webbing near the buckle a
quick upward pull - the buckle should remain securely locked.
2. With the seat belt unfastened, unreel the webbing to the limit of
its travel. Check that unreeling is free from snatches and snags.
3. With the webbing half unreeled, hold the tongue plate and give
it a quick forward pull - the mechanism must lock automatically
and prevent any further unreeling.
If a seat belt should fail any of these tests, contact your dealer
immediately.
SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONERS
The seat belt pre-tensioners act in conjunction with the airbag SRS
system and provide additional protection in the event of a severe
frontal impact on the vehicle (see ’Airbag SRS’). The pre-tensioners
automatically retract the seat belts fitted to the front seats. This
reduces any slack in both the lap and diagonal portions of the belts,
thereby reducing forward movement of the belt wearer in the event
of a severe frontal collision.
The airbag SRS warning light on the instrument panel, described on
the following page, will alert you to any malfunction of the seat belt
pre-tensioners.
WARNING!
Always replace a seat belt
assembly that has
withstood the strain of a
severe vehicle impact, or
one where the webbing
shows signs of fraying.
For Your Safety .........
DO NOT wear seat belts fitted
with pre-tensioners directly
over bare skin. In the event of a
collision, friction burns could
occur when the pre-tensioners
are activated.
Operating Tip ..........
If the pre-tensioners have been
activated, the seat belts will still
function as conventional
restraints. If it is necessary for
the car to be driven to a dealer
for repair, the seat belts must
be worn.