40
Chapter 1 Performance
Chapter 1
Adjusting the Sound to Achieve the
Preferred Tone Quality (Equalizer)
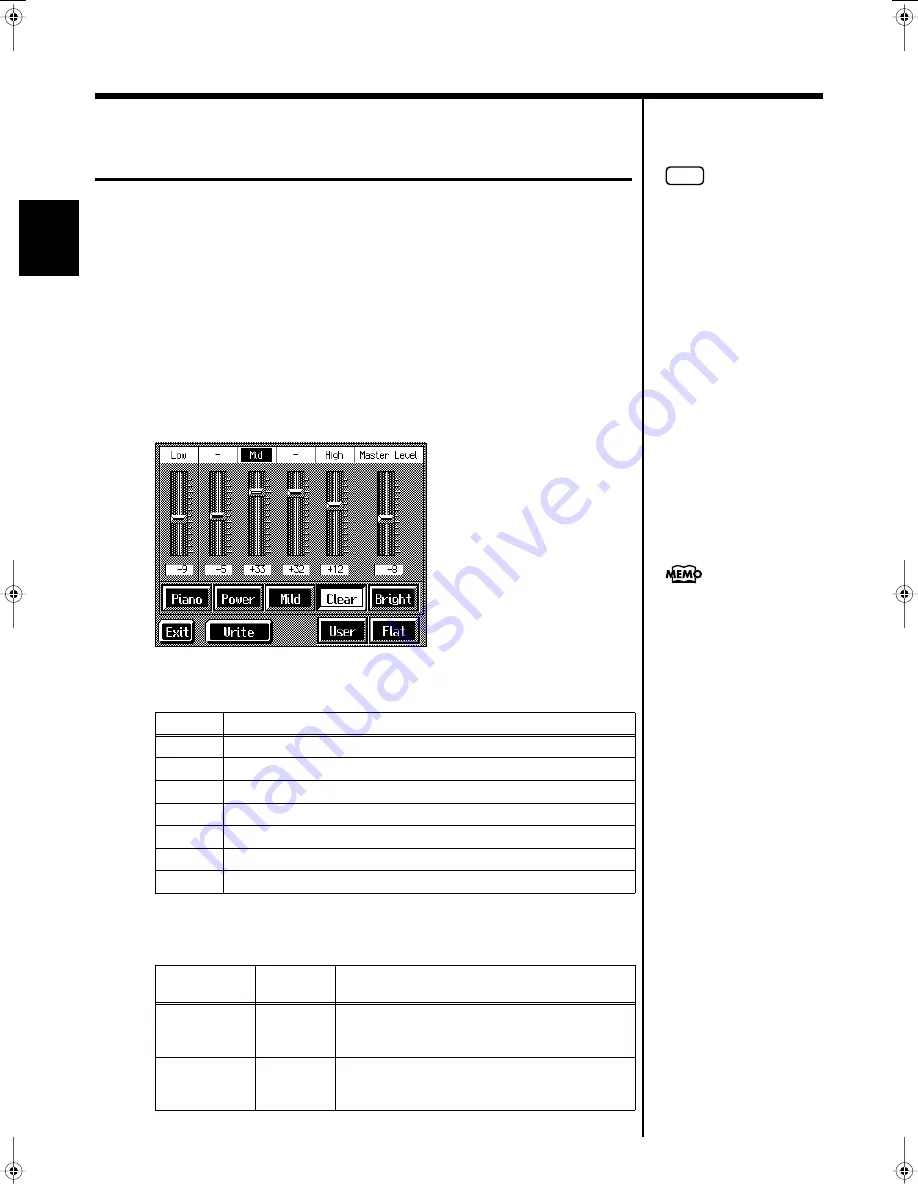
The KR features a built-in, five-band digital equalizer.
An equalizer boosts or cuts specific sound pitches (frequency ranges) to adjust the
sound balance for the overall performance. For example, you can boost the highs to
get a crisper sound, or boost the low end for a more powerful sound.
You can also adjust the sound to compensate for the acoustical characteristics of the
performance space.
If raising the slider for each frequency ends up distorting the sound, you can correct
the distortion with the Master Level slider.
1.
Press the [Equalizer] button.
The “Equalizer screen” appears.
fig.d-eq.eps_60
2.
Touch the Type icon to make your selection.
3.
Touch the slider to make adjustment.
Display
Explanation
Piano
The optimal settings for piano performance are selected.
Power
Boosts both the low- and high-frequency ranges.
Mild
Lows and highs are restrained for a pleasant-sounding tone.
Clear
This setting slightly boosts the midrange for a simple pop feeling.
Bright
This setting boosts the high frequencies for a brilliant, sparkling sound.
Flat
All slider values are set to “0.”
User
Store your own preferred settings (p. 41).
Displayed
Settings
Value
Explanation
Low
-60–0–+60
Low-frequency range. This is the range of
frequencies for instruments like drums, bass,
organ, guitar and strings.
–
-60–0–+60
Mid-low-frequency range. This is the range of
frequencies for lower brass and woodwind
instruments.
NOTE
Raising the overall volume
with the Master Level slider
and the [Volume] knob when
the frequency sliders are
already at high levels not only
may distort the sound and
cause ear pain, it can also place
unreasonable strain on the
built-in speakers and internal
circuitry. Use the KR at a
moderate volume level.
When <Flat> is selected (when
all sliders are at “0”), then even
when [Equalizer] is pressed,
the indicator does not light up.
KR-17_15_e.book 40 ページ 2004年12月6日 月曜日 午後1時54分






























