RADIUS
Product
Description
PDR 121
iom_pdr121_04_r02.doc
Rev 02
Page 2 (67)
Contents
1
General ________________________________________________________________ 4
1.1
Document History________________________________________________________________ 4
1.2
RADIUS Contact Information _______________________________________________________ 4
2
Find Your Way in The Manual ______________________________________________ 5
3
Introduction _____________________________________________________________ 6
3.1
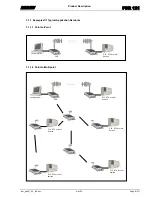
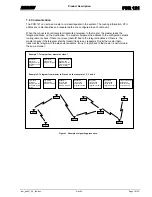
Typical Application Areas__________________________________________________________ 7
3.1.1
Examples Of Typical Application Networks __________________________________________________8
4
Technical Specifications _________________________________________________ 11
5
Quick Start Guide _______________________________________________________ 12
6
Glossary Of Terms ______________________________________________________ 13
6.1
dBm to W Conversion Table ______________________________________________________ 14
7
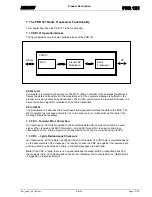
The PDR 121 Radio Transceiver Functionality________________________________ 15
7.1
PDR 121 Operation Blocks _______________________________________________________ 15
7.2
FEC - Forward Error Correction____________________________________________________ 15
7.3
CRC – Cyclic Redundancy Checksum ______________________________________________ 15
7.4
Communication ________________________________________________________________ 16
7.5
Radio Receiver Sensitivity ________________________________________________________ 17
7.5.1
PDR 121 Receiver Sensitivity____________________________________________________________17
7.6
Radio Transmitter Power _________________________________________________________ 17
7.7
RSSI – Received Signal Strength Indication __________________________________________ 18
7.8
Differences between PDR 121 Models ______________________________________________ 19
8
Operating the PDR 121 ___________________________________________________ 20
8.1
LED Indicators and Connectors ____________________________________________________ 20
8.2
Peer-To-Peer __________________________________________________________________ 21
8.3
Collision Avoidance _____________________________________________________________ 21
8.4
Remote frequency change________________________________________________________ 23
8.5
Remote Tx power change ________________________________________________________ 24
8.6
Multiple RTU addressing to one radio _______________________________________________ 24
8.7
Radio Link Test ________________________________________________________________ 24
8.8
Split transmitting and receiving frequencies __________________________________________ 24
8.9
Split Tx Uplink Frequency ________________________________________________________ 25
8.9.1
Split Tx Uplink Example Network _________________________________________________________25
8.10
Repeating Alternative Systems _________________________________________________ 26
9
Installation_____________________________________________________________ 27
9.1
General ______________________________________________________________________ 27
9.2
Power Supply __________________________________________________________________ 27
9.2.1
Recommended minimum demands: _______________________________________________________27
9.3
Battery Power Supply ___________________________________________________________ 28
9.4
Serial Interface _________________________________________________________________ 29
9.4.1
PDR 121 Serial Interface Characteristics ___________________________________________________29
9.4.2
Serial Cable Configurations _____________________________________________________________30
9.4.3
EIA RS323 Conversion Table ____________________________________________________________33
9.5
Cabinet Mounting _______________________________________________________________ 34
9.5.1
PDR 121 mounted in cabinet ____________________________________________________________34
10
Accessories____________________________________________________________ 35
11
Radio Networking _______________________________________________________ 36
11.1
Antennas __________________________________________________________________ 36
11.1.1
Antenna Gain _______________________________________________________________________36
11.1.2
Antenna Types ______________________________________________________________________37
11.1.3
Antenna Gain versus Radio Output Power _________________________________________________38
11.2
Fade Margin ________________________________________________________________ 39
11.3
Radio Link Calculations _______________________________________________________ 40
11.3.1
No Line of Sight Calculations ___________________________________________________________40
11.3.2
Line Of Sight Calculations______________________________________________________________43
12
Configuration __________________________________________________________ 45
12.1
Equipment _________________________________________________________________ 45
12.2
Getting Started ______________________________________________________________ 45
12.3
Configuration Menus Overview _________________________________________________ 46