108
--
--
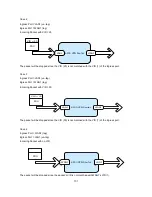
0
Reliability
Normal
--
--
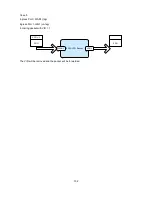
1
Reliability
High
The standardized DiffServ field of the packet is marked with a value so that the packet receives a particular
forwarding treatment at each network node.
RFC 2597 defines the assured forwarding (AF) classes. There are four AF classes, AF1x through AF4x.
Within each class, there are three drop probabilities. Depending on a given network's policy, packets can be
selected for a PHB based on required throughput, delay, jitter, loss, or according to priority of access to
network services.
Classes 1 through 4 are referred to as AF classes.
The following table illustrates the DSCP coding for specifying the AF class with the probability. Bits 0, 1, and
2 define the class; bits 3 and 4 specify the drop probability; bit 5 is always 0.
Class 1
Class 2
Class 3
Class 4
Low Drop
001010
AF11
DSCP 10
010010
AF21
DSCP 18
011010
AF31
DSCP 26
100010
AF41
DSCP 34
Medium Drop
001100
AF12
DSCP 12
010100
AF22
DSCP 20
011100
AF32
DSCP 28
100100
AF42
DSCP 36
High Drop
001110
AF13
DSCP 14
010110
AF23
DSCP 22
011110
AF33
DSCP 30
100110
AF43
DSCP 38
The recommended DSCP values which are based on RFC 4594 are in the following table:
Service Class Name DSCP Name DSCP Value
Application Examples
Network Control and
OAM
CS6
110000 (48)
Network routing and OAM (e.g. SNMP,
Ethernet CFM, proprietary NMS traffic)
Signaling
CS5
101000 (40)
Signaling (e.g. H.323, SIP)
Telephony
EF
101110 (46)
IP Telephony bearer
Multimedia
Conferencing
AF41, AF42,
AF43
100010 (34), 100100
(36),
100110(38)
Videoconferencing
Real-Time
CS4
100000 (32)
Interactive control (e.g. CAM), real-time