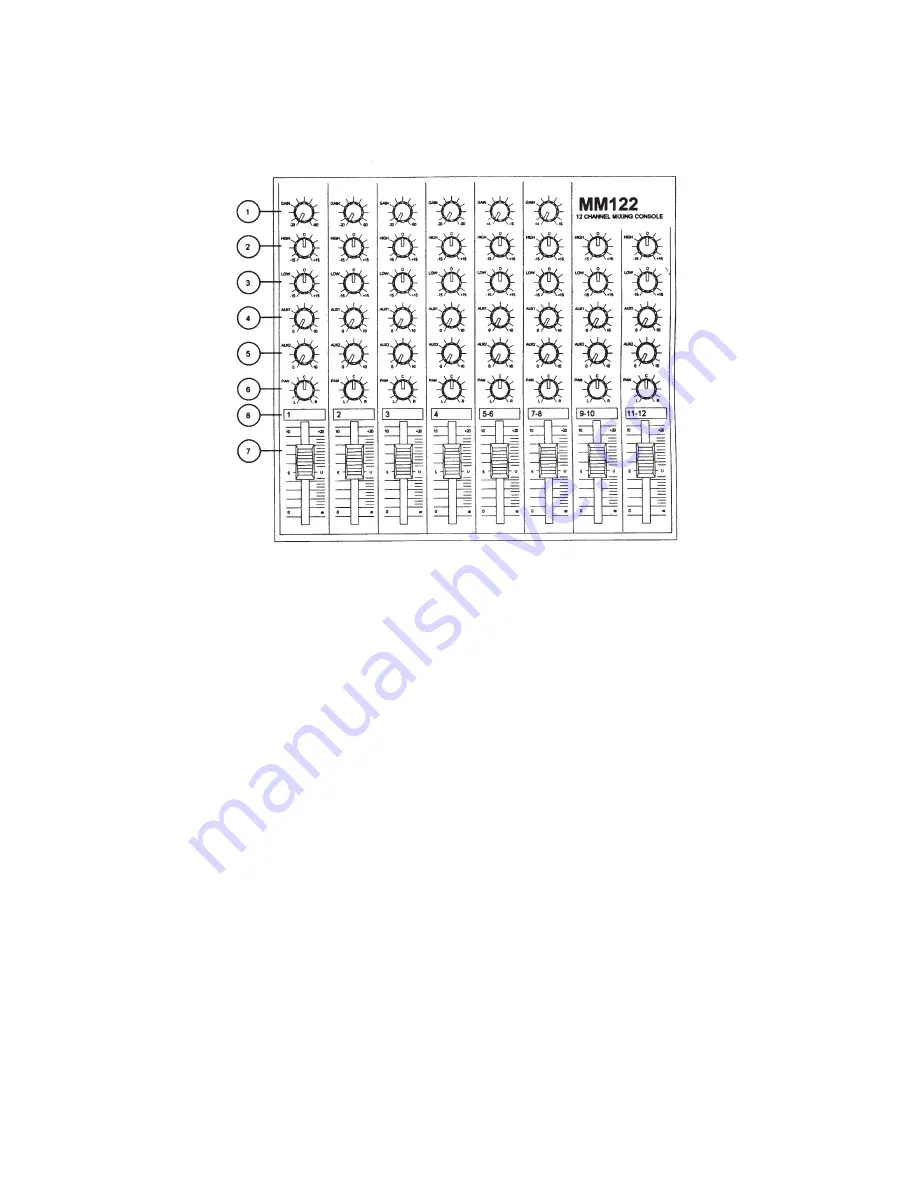
!
CHANNEL STRIP
1. Input gain control
This control brings the incoming signal to the
optimal level for the mixer to work with. It works
in conjunction with the LED ladder (9).
Boosting a signal too much will overload the cir-
cuitry and cause the sound to distort. A signal
that is not boosted enough results in a lower
overall sound to noise ratio. By adjusting this
control properly, the signal (your music) will be
at its strongest compared to the background
noise.
Channels 9-10 and 11-12 have no input gain
control. However, most stereo devices have an
output gain control that can be used instead to
set the level coming in to the mixer. Generally,
just set it to maximum because the MM122 has
enough headroom to handle high input levels
without clipping. in most cases you will be able
to arrange your gear so that any stereo devices
without output gain are put on channels 5-6 and
FRONT-PANEL DESCRIPTION
7-8, and can use the MM122's input gain
controls.
2. Hi EQ
High EQ, or equalization, affects the high fre-
quency content of the sound. Technically this is
up to a 15dB cut/boost shelving at 12kHz. Even
a sweet sounding EQ like the MM122's is best
if used sparingly - and remember to cut as well
as boost. It is good practice to try and achieve
the desired sound by adjusting the instrument,
mic position, etc. rather than resorting to an elec-
tronic 'fix'. The 'zero' or 'flat' position for all the
EQ controls is at 12 O'clock.
3. Low EQ
This affects the low frequencies in the same
way the Hi EQ affects the highs. A 15dB
boost/cut shelving at 80Hz. Increases can
bring up kickdrums and bass, and cuts are
All manuals and user guides at all-guides.com





































