AMPLIFIER BOARD
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Class-D Amplifier circuit description ................................................. 8-1
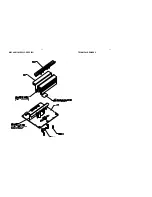
Exploded view ................................................................................... 8-2
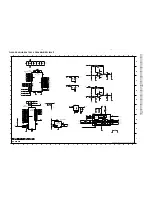
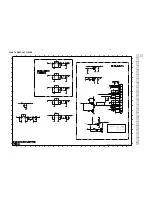
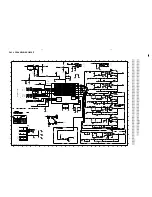
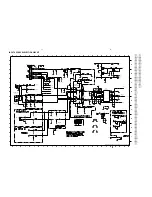
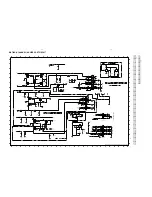
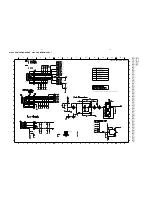
Class-D Amplifier Board- Circuit Diagram Part 1 .............................. 8-3
Class-D Amplifier Board- Circuit Diagram Part 2 .............................. 8-4
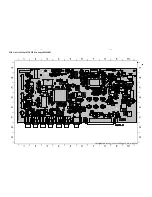
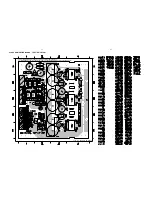
Class-D Amplifier Board- Top View Layout ....................................... 8-5
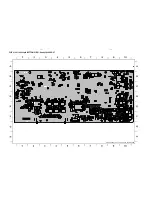
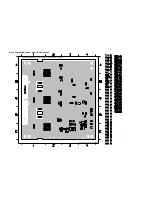
Class-D Amplifier Board- Bottom View Layout ................................. 8-6
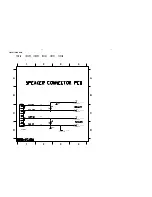
Electrical parts list - Amplifier board ................................................. 8-7
8-1
8-1
6-channel class-D amplifier
Basic operation of a class-D amplifier
Basically, the output stage of a class-D amplifier outputs a continuous square wave swinging between positive and negative power supplies
with a fixed frequency (“clock” frequency) far beyond the audible range. The duty cycle of this square wave is modulated with the audio signal.
The output is followed by a low-pass filter which eliminates the clock frequency and allows only the audio signal going to the speaker. See
simplified drawing below.
Compared to a conventional power amplifier the benefits of the Class-D amplifier are:
• higher effiency
• lower power dissipation
• smaller heatsink required
• smaller mains transformer required
The main disadvantage of this concept is:
• The amplifier is operating with a high-frequency square wave at high amplitude and currents. This requires special precautions to prevent
excessive electromagnetic ratiation (EMC).
Summary of Contents for LX2600D
Page 33: ...7 11 7 11 PCB 31311352 pt3 TOP VIEW MAPPING ...
Page 35: ...7 13 7 13 PCB 3139 113 3522 pt3 BOTTOM VIEW MAPPING ...
Page 38: ...8 2 8 2 MECHANICAL EXPLODED VIEW 0010 0006 TECHNICAL REMARKS ...
Page 47: ...MAIN ENCASING EXPLODED VIEW 10 1 10 1 ...