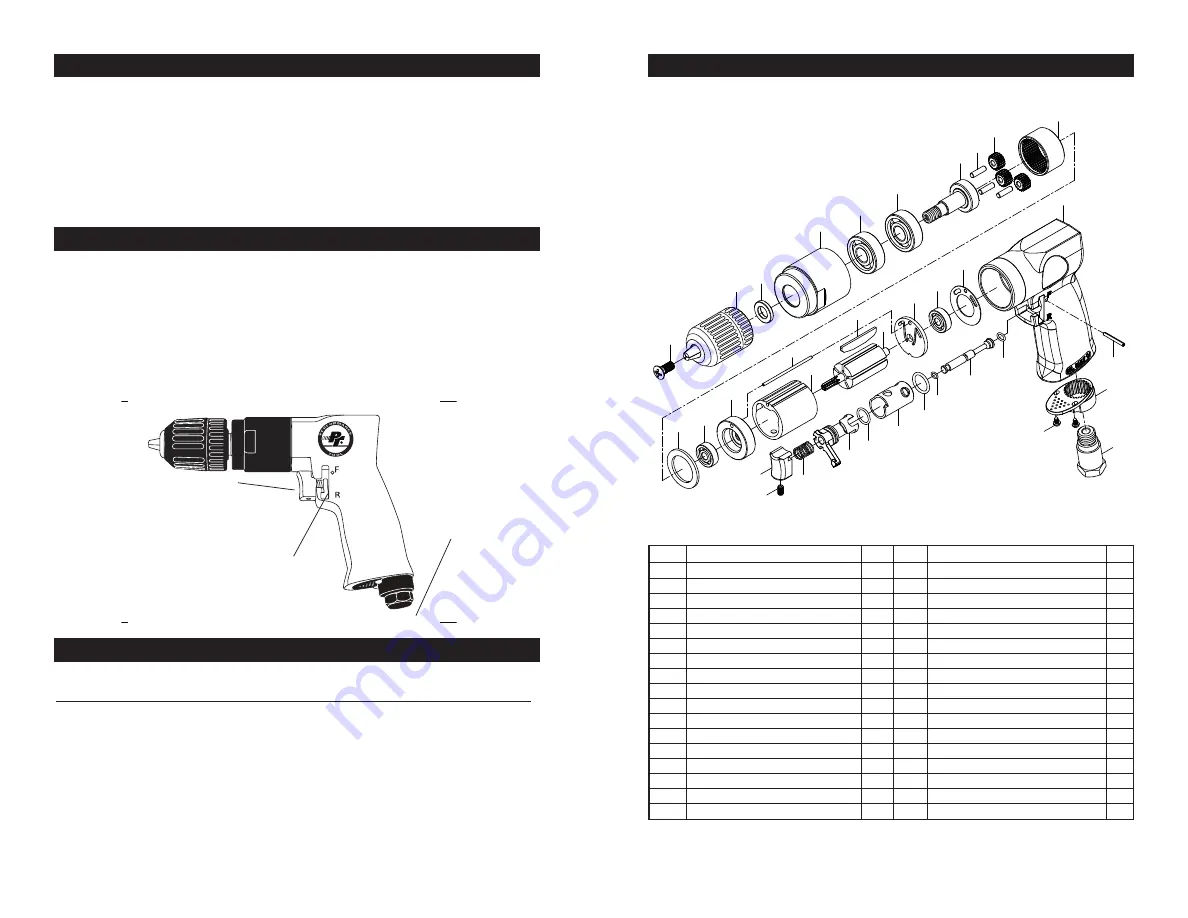
1
Housing
1
2
O-Ring
1
3
Switch Pin
1
4
O-Ring
1
5
O-Ring
1
6
Bushing
1
7
O-Ring
1
8
Direction Lever
1
9
Spring
1
10
Trigger
1
11
Trigger Nut
1
12
Trigger Pin
1
13
Exhaust Diffuser
1
14
Screw
2
15
Air Inlet
1
16
Seal Gasket
1
17
Rear Bearing
2
18
Rear Cover
1
19
Rotor
1
20
Rotor Blade
5
21
Cylinder
1
22
Fixed Pin
1
23
Front Cover
1
24
V-Gasket
1
25
Gear Ring
1
26
Gear
3
27
Gear Pin
3
28
Spindle
1
29
Bearing
2
30
Clamp Nut
1
31
Bushing
1
32
3/8 in. Chuck
1
33
Chuck Screw
1
PARTS LIST
33
32
31
30
29
29
28
27
26
25
33
24
17
23
22
20
21
19
18
17
16
10
11
9
8
7
6
4
3
5
2
12
13
15
14
INDEX DESCRIPTION
QTY INDEX DESCRIPTION
QTY
3
4
1. Use of a center punch to mark the starting point of a hole is recommended when drilling
metals with this tool. Place drill against work before starting motor. Do not apply too much
pressure to the drill as this can cause the bit to overheat and break. When the hole is drilled,
do not stop the drill until it is withdrawn from work.
2. If the drill should bind and stop inside the work, release the trigger immediately and
determine the cause. If removal of bit from the drill is necessary, disconnect the drill from the
air source before removing. Do not attempt to free the bit by forcing it with the drill.
3. A forward and reverse lever permits the tool to run in a forward (clockwise) rotation or in
reverse (Counter-clockwise) rotation. Do not attempt to change direction while tool is running.
OPERATION
Clean air of correct air pressure is recommended for the power supply for this tool. A maximum
of 90 PSI at the tool is recommended for most air tools of this class. Check specifications
section for recommended pressure. (Depending on length of air hose and other circumstances,
air pressure at compressor may need to be increased to 100 PSI to ensure 90 PSI at the tool.)
Water in the air hose and compressor tank contributes to reduced performance and damage of
the air tool. Drain the air tank and filters before each use and as necessary to keep the air
supply dry.
Hose length over 25’ causes loss in line pressure. Increase hose I.D. or increase compressor
pressure to compensate for the pressure loss. Use an in-line pressure regulator with gauge if air
inlet pressure is critical.
AIR SOURCE
Forward/Reverse Lever
Air Inlet
Trigger
INSUFFICIENT POWER:
Probable Cause
Solution
Dirty or clogged air passages......... Flush and lubricate tool, drain air tank and supply line
Insufficient air supply ...................... Increase line pressure, Make sure compressor
matches tool's air pressure and consumption needs
Air leakage ...................................... Use PTFE tape at all fittings and joints. Check tool for
worn or damaged O-rings & seals.
Worn/damaged wear & tear parts .. Replace as necessary.
Tool matching ................................. Be sure you are using a tool suited for the torque
requirements of the job at hand.
TROUBLESHOOTING





















