Model No. WA-9857
Experiment 1: Wave Speed
15
®
Wave Speed Calculated from Tension and String Density
You can also calculate the wave speed from the tension (F) and the linear density (
µ
) of the cord
with:
(eq. 2)
The linear density is the mass per unit length of the cord when it is stretched. This will be less than
the value that you calculated for the unstretched cord. You will now calculate the stretched linear
density.
1.
Unhook the cord from the Force Sensor and measure its unstretched length (from the String
Vibrator blade to the loop on the other end).
2.
Calculate the stretched density using the formula:
3.
Calculate the speed of the wave from your values of F and
µ
.
Speed of a Single Pulse
Another way to find the wave speed is to measure the speed of a single pulse. You will use the
force sensor and the voltage sensor, to time a pulse traveling down the cord.
1.
Unplug the power supply from the String Vibrator. Connect the voltage sensor to the power
input of the String Vibrator.
2.
Set the sampling rates of force sensor and the voltage sensor to 1000 Hz.
3.
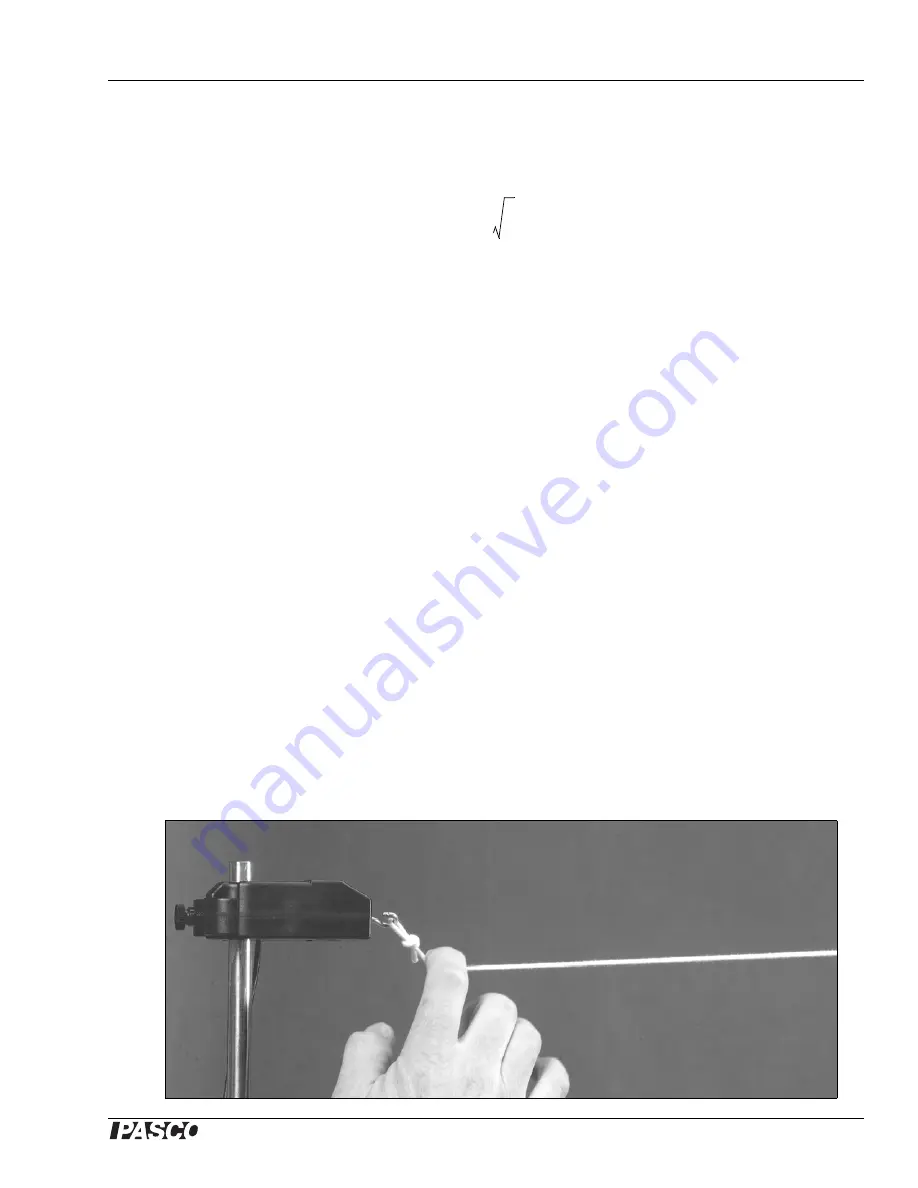
To activate the wave, pluck the string vertically as close as possible to the force sensor (as
shown in the picture). Notice that when the pulse reaches the String Vibrator, it makes the
blade move up and down; this motion moves a magnet inside a coil, which generates a
voltage spike that the voltage sensor will measure.
v
F
µ
---
=
Stretched Linear Density
µ
Unstretched Length
(
)
Stretched Length
(
)
----------------------------------------------------
Unstretched Linear Density
(
)
×
=
=
Summary of Contents for WA-9857
Page 26: ......












































