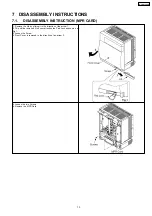
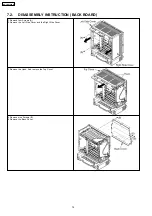
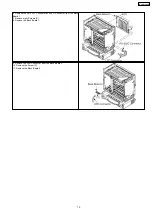
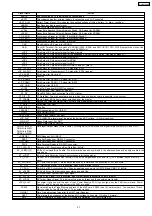
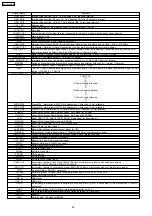
Signal Name
Function
nBACK
Bus Acknowledge: This indicates Bus Acknowledge.
nBATT
This indicates whether external battery is connected or not.L: Connected
nBAT_ALM
Battery Alarm Signal: This indicates the declined voltage of lithium battery. (L: Alarm condition)
nBREQ
Bus Request: Bus request signal
nBS
Bus Cycle Start: Bus cycle start signal
nCASL
Lower Byte Address Column Address Strobe: CAS signal for SDRAM
nCASU
Upper Byte Address Column Address Strobe: CAS signal for SDRAM
CH_SEL[0]
Synchronous Signal for CODEC (For MOH#1/Page#1)
CH_SEL[1]
Synchronous Signal for CODEC (For MOH#2/Page#2)
CH_SEL[2]
Synchronous Signal for CODEC (For RMT)
CKE
Clock Enable: CKE signal for SDRAM
CKIO
Clock I/O Terminal: For bus clock of SDRAM (IC305, IC306) and ASIC (IC101) CPU (IC100) outputs the clock of four
times frequency as many as Source clock (16.384MHz).
nCS0
Chip Select 0: Chip select signal for flash memory
nCS2
Chip Select 2: Chip select signal for the expanded SDRAM (Future Option, Reserve at present.)
nCS3
Chip Select 3: Chip select signal for SDRAM
nCS4
Chip Select 4: Chip select signal for SRAM
nCS5
Chip Select 5: Chip select signal for ASIC
nCS6
Chip Select 6: Chip select signal for USB I/F and SD card I/F
nCS_FLASH0
Chip Select for Flash memory0: CS signal for IC303
nCS_FLASH1
Chip Select for Flash memory1: CS signal for IC304 (reserve)
nCS_SDB0
Chip Select for Sd card I/F
nCS_SDB1
Reserve
nCS_SRAM0
Chip Select for SRAM0: CS signal for IC301
nCS_SRAM1
Chip Select for SRAM1: CS signal for IC302
nCS_USB
Chip Select for USB I/F
nCTS2
Clear To Send from RS-232C connector
CTS_RMT
Clear to Send: Flow signal for modem
CT_C8
Clock8.192MHz clock outputted from PLL master
CT_D[0] -[7]
CT Data Bus: Two-way serial data bus to which the drive from any card is possible in the system.
CT_FRAME
Frame Signal: 8KHz frame signal outputted from the master
CT_NETREF
Backup Synchronous Signal (MAX 2MHz) 8KHz signal output from slave etc.
C_CS[0]
Chip Select For RMT
D[0] -D[31]
Data Bus
nDACK0-1
DMA Acknowledge: For USB I/F
DCD2
Data Carrier Detect
DCLK_RMT
Codec Clock (8MHz): For RMT
nDC_ALM
DC ALARM:DC alarm signal; Indicates the declined DC voltage. (L: Alarm condition)
DIN_RMT
Codec Data Input: For RMT
DOUT_RMT
Codec Data Output: For RMT
DQMLL (nWE0)
DQMLU (nWE1)
DQMUL (nWE2)
DQMUU (nWE3)
Data Input/Output Mask (Write Enable): DQM signal for SDRAM and WE signal for each memory IC and ASIC
nDREQ0-1
DMA Request: For USB I/F
DSR2
Data Set Ready from RS-232C connector
DSR_RMT
Data Set Ready from RS-232C connector
DTR2
Data Terminal Ready to RS-232C connector
EC_AD[0] -[15]
Address of EC Synchronous Bus, Data Bus (4MHz)
EC_nCBE[1]-[0]
EC Bus Command/Byte Enable: The initiator drives as bus command in the address phase and as byte enable in the
data phase.
EC_nCDET
EC Line Card Detection Signal Asynchronous interrupting signal
EC_CLK
Clock of EC Synchronous Bus (8MHz) All the EC bus signal except nRESET/EC_INT operates in sync with this
signal.
EC_nFRAME
EC Cycle Frame Signal: This indicates the drive by initiator and the execution of ECI bus cycle.
EC_nINT
EC Interrupting Signal: This is asserted, when slave interrupt occurs.
EC_PAR
Parity Bit of EC Synchronous Bus: Drive by applying even parity to AD[15:0] and CBE[1:0]. (4MHz)
EC_nPERR
EC Parity Error: Flag indicating error status by parity flag
EC_nRST
EC Reset Input: System reset input signal
EC_nSTOP
EC Bus Stop Signal: This is asserted, when target requests transaction halt to initiator.
EC_nTRDY
EC Target Ready Signal: This indicates the drive by target and the possible data transfer.
nFAN_ALM
Fan Alarm: It goes Low at the error of the L Power Supply’s FAN. It goes High when the FAN is normal and, Power
Supply S and M, which does not carry the FAN, are used.
FSEL0
Signal switching the Flash Memory address of the MEX card. FSEL0 is set by hard jumper.L: The number of Flash
Memory chips on the MPR is 1pc. H: The number is 2pcs.
GAIN0-1
Gain: Gain adjustment signal for the RMT card (Reserve)
HALT
This alarms the occurrence of the declined DC voltage to line card. H: Active L: Normal
nINIT
System Initialization Switch Input: L: At system initialization, H: At normal start-up
27
KX-TDA100CE
Summary of Contents for TDA 100
Page 8: ...5 SYSTEM OVERVIEW 5 1 SYSTEM CONFIGURATIONS 8 KX TDA100CE ...
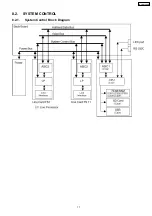
Page 17: ...8 2 SYSTEM CONTROL 8 2 1 System Control Block Diagram 17 KX TDA100CE ...
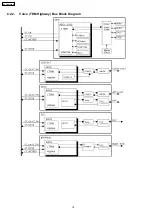
Page 18: ...8 2 2 Voice TDM Highway Bus Block Diagram 18 KX TDA100CE ...
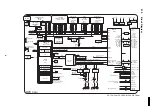
Page 21: ...8 3 2 EC Bus System Connection Diagram 21 KX TDA100CE ...
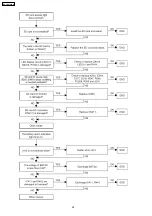
Page 32: ...11 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 11 1 MPR CARD 11 1 1 Startup 32 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 33: ...33 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 34: ...34 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 35: ...35 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 36: ...36 KX TDA100CE ...
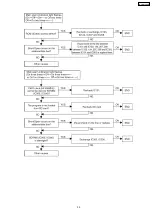
Page 37: ...11 1 2 Phone Call 37 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 38: ...11 1 3 Paging 38 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 39: ...39 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 40: ...40 KX TDA100CE ...
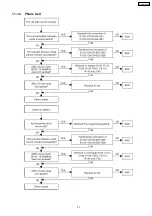
Page 41: ...11 1 4 MOH Using 41 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 42: ...42 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 43: ...43 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 44: ...11 1 5 USB Connection 44 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 45: ...45 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 46: ...11 1 6 RS 232C Connection 46 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 47: ...47 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 48: ...11 1 7 SD Card I F 48 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 49: ...11 1 8 Other 49 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 54: ...12 2 DIAGNOSIS TEST 1 Click Diagnosis of Utility 54 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 55: ...2 Pair Port Test operation Select card for Test 3 Click Pair Port Test 55 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 56: ...4 Click OK 5 Click Cancel 56 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 57: ...6 Card Test operation Select card for Test 7 Click Card Test 57 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 58: ...8 Click OK 9 Click Cancel 58 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 63: ...14 TERMINAL GUIDE OF ICS TRANSISTORS AND DIODES 63 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 65: ...16 CABINET AND ELECTRICAL PARTS LOCATION 65 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 66: ...16 1 EXTENSION BOARDS FOR SERVICING 66 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 67: ...17 ACCESSORIES AND PACKING MATERIALS 67 KX TDA100CE ...
Page 86: ...Waveform 7 Waveform 8 20MHz 12MHz KX TDA100CE 86 ...
Page 91: ...91 KX TDA100CE A KXTDA100CE ...