Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor
Design, Specifications are subject to change without notice. Ask factory for technical specifications before purchase and/ or use.
Whenever a doubt about safety arises from this product, please inform us immediately for technical consulation without fail.
–
EE18
–
1.3 Common Application Conditions to Avoid
The following misapplication load conditions will
c a u s e ra p i d d e t e r i o r a t i o n t o c a p a c i t o r e l e c t r i c a l
p a r a m e t e r s. l n a d d i t i o n , ra p i d h e a t i n g a n d g a s
generation within the capacitor can occur causing
the pressure relief vent to operate and resuItant
leakage of electrolyte. Under extreme conditions,
explosion and fire could result. Leakinq electrolyte
is combustible and electrically conductive.
(1) Reverse Voltaqe
DC capacitors have polarity. Verify correct polarity
before inser tion. For circuits with changing or
uncer tain polarity,use DC bipolar capacitors. DC
bipolar capacitors are not suitable for use in AC
circuits.
(2) Charqe/Discharqe Applications
Standard capacitors are not suitable for use in
repeating charge/discharge applications. Fo r
charqe/discharqe applications consult us and advise
actual conditions.
(3) Overvoltage
Do not appIy voltaqes exceeding the maximum
specified rated voltages. Voltage up to the surge
voltage rating are acceptable for shor t periods of
time. Ensure that the sum of the DC voltage and
the super imposed AC r ipple vo l t a g e does not
exceed the rated voltage.
(4) Ripple Current
Do not apply ripple currents exceeding the maximum
specified value. For high ripple current applications,
use a capacitor designed for high rippIe currents
or contact us with your requirements.
Ensure that allowable ripple currents superimposed
on low DC bias voltages do not cause reverse voltage
conditions.
1.4 Using Two or More Capacitors in Series
or Parallel
(1) Capacitors Connected in Parallel
The circuit resistance can closely approximate the
ser ies resistance of the capacitor causing an
i m b a l a n c e o f r i p p l e c u r r e n t l o a d s w i t h i n t h e
capacitors. Careful design of wiring methods can
minimize the possibility of excessive ripple currents
applied to a capacitor.
(2) Capacitors Connected in Series
Nor mal DC leakage curren t differences among
capacitors can cause voltage imbalances. The use
of voltage divider shunt resistors with consideration
to leakage currents, can prevent capacitor voltage
imbaIances.
1.5 Capacitor Mounting Considerations
(1) DoubIe - Sided Circuit Boards
Avoid wir ing Patter n r uns which pass between
the mounted capacitor and the circuit board. When
dipping into a solder bath, excess solder may collect
u n d e r t h e c a p a c i t o r b y c a p i l l a r y a c t i o n a n d
shortcircuit the anode and cathode terminals.
(2) Circuit Board Hole Positioning
The vinyl sleeve of the capacitor can be damaged
i f s o l d e r p a s s e s t h r o u g h a l e a d h o l e f o r
subsequently processed parts. Special care when
locating hole positions in proximity to capacitors is
recommended.
(3) Circuit Board Hole Spacing
The circuit board holes spacing should match the
capacitor lead wire spacing within the specified
tolerances. Incorrect spacing can cause excessive
lead wire stress during the insertion process. This
may resuIt in premature capacitor failure due to
short or open circuit, increased leakage current,
or electrolyte leakage.
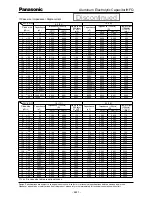
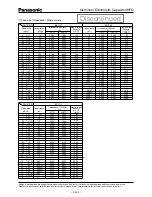
(4)Land/Pad Pattern
The circuit board land/pad pattern size for chip
capacitors is specified in the following table.
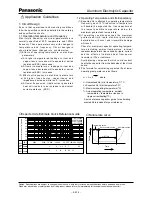
[ Table of Board Land Size vs. Capacitor Size ]
Among others, when the size a is wide , back fillet can
not be made, decreasing fitting strength.
❉
Decide considering mounting condition, solderability
and fitting strength, etc. based on the design
standards of your company.
b a b
c
Board land part
Size
A(
φ
3)
B(
φ
4)
C(
φ
5)
D(
φ
6.3)
E(
φ
8 x 6.2L)
F(
φ
8 x 10.2L)
G(
φ
10 x 10.2L)
a
0.6
1.0
1.5
1.8
2.2
3.1
4.6
b
2.2
2.5.
2.8
3.2
4.0
4.0
4.1
c
1.5
1.6
1.6
1.6
1.6
2.0
2.0
(mm)