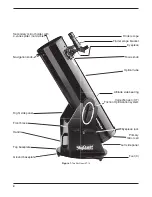
13
covered until the Sun sets so the tube does not heat greatly
above the temperature of the outside air.
The SkyQuest XT10 has the ability to mount a small fan to
make cooling the tube faster. On the bottom of the mirror cell
there are four threaded holes (M4-.7) where a fan can be
attached. Orion sells a fan for the SkyQuest XT10; consult
the Orion catalog or telescope.com for details.
D. Let Your Eyes Dark-Adapt
Do not expect to go from a lighted house into the darkness
of the outdoors at night and immediately see faint nebulas,
galaxies, and star clusters - or even very many stars, for that
matter. Your eyes take about 30 minutes to reach perhaps
80% of their full dark-adapted sensitivity. Many observers
notice improvements after several hours of total darkness. As
your eyes become dark-adapted, more stars will glimmer into
view and you will be able to see fainter details in objects you
view in your telescope. Exposing your eyes to very bright day-
light for extended periods of time can adversely affect your
night vision for days. So give yourself at least a little while to
get used to the dark before you begin observing.
To see what you are doing in the darkness, use a red-filtered
flashlight rather than a white light. Red light does not spoil
your eyes’ dark adaptation like white light does. A flashlight
with a red LED light is ideal, or you can cover the front of a
regular incandescent flashlight with red cellophane or paper.
Beware, too, that nearby porch and streetlights and automo-
bile headlights will spoil your night vision.
Tracking Celestial Objects
The Earth is constantly rotating about its polar axis, com-
pleting one full rotation every 24 hours; this is what defines
a “day”. We do not feel the Earth rotating, but we can tell that
it is at night by seeing the apparent movement of stars from
east to west. This movement translates into a rate of approxi-
mately .25° per minute, or 15 arc-seconds per second. (There
are 60 arc-minutes in 1°, and 60 arc-seconds in one arc-min-
ute.) This is called the sidereal rate.
When you observe any astronomical object, you are watching
a moving target. This means the telescope’s position must be
slowly updated over time to keep an object in the field of view.
To keep the object in the telescope’s field of view (to “track”
it), the telescope must be moved by small increments every
now and then, in the direction the object is moving. This is
easy to do with a SkyQuest XT10 Dobsonian because of its
buttery smooth motion on both axes. As the object moves off
toward the edge of the field of view, you just lightly nudge the
telescope to bring it back to the center.
You will notice that it is more difficult to track objects when the
telescope tube is aimed nearly straight up. This is inherent to
the basic design of the Dobsonian, and stems from the fact
that there is very little leverage to move in azimuth when the
tube is in a near-vertical position. To gain more leverage, try
grasping the tube close to the altitude side bearings with both
hands. Also, when looking overhead, if the telescope cannot
be moved any more in altitude, rotate the telescope 180° in
azimuth to continue motion.
Remember that objects appear to move across the field of
view faster at higher magnifications. This is because the field
of view becomes narrower.
Eyepiece Selection
By using eyepieces of varying focal lengths, it is possible
to attain many magnifications with the SkyQuest XT10
Dobsonian. The telescopes come with two high-quality
SiriusPlössl eyepieces: a 25mm, which gives a magnification
of 48x, and a 10mm, which gives a magnification of 120x.
Other eyepieces can be used to achieve higher or lower
powers. It is quite common for an observer to own five or
more eyepieces to access a wide range of magnifications.
This allows the observer to choose the best eyepiece to use
depending on the object being viewed. At least to begin with,
the two supplied eyepieces will suffice nicely.
Whatever you choose to view, always start by inserting your
lowest power (longest focal length) eyepiece to locate and
center the object. Low magnification yields a wide field of
view, which shows a larger area of sky in the eyepiece. This
makes acquiring and centering an object much easier. If you
try to find and center objects with high power (narrow field of
view), it’s like trying to find a needle in a haystack!
Once you’ve centered the object in the eyepiece, you can
switch to higher magnification (shorter focal length eyepiece),
if you wish. This is especially recommended for small and
bright objects, like planets and double stars. The Moon also
takes higher magnifications well.
Deep-sky objects, however, typically look better at medium
or low magnifications. This is because many of them are
quite faint, yet have some extent (apparent width). Deep-sky
objects will often disappear at higher magnifications, since
greater magnification inherently yields dimmer images. This
is not the case for all deep-sky objects, however. Many galax-
ies are quite small, yet are somewhat bright, so higher power
may show more detail.
The best rule of thumb with eyepiece selection is to start
with a low power, wide field, and then work your way up in
magnification. If the object looks better, try an even higher
magnification. If the object looks worse, then back off the
magnification a little by using a lower power eyepiece.
Use of 2" Eyepieces
The SkyQuest XT10 comes with a large format focuser
(Figure 9) as standard equipment. Because of its large size, it
is able to accept eyepieces that have a 2" barrel diameter. 2"
eyepieces are desirable because they allow for a wider field
of view than 1.25" eyepieces. Many observers own at least
one 2" eyepiece to yield the largest field of view possible for
looking at wide deep sky objects, such as open star clusters
and gaseous nebulae. 2" eyepieces can also give nice views
of the Moon.
To use a 2" eyepiece, simply remove the 1.25" eyepiece
adapter from the end of the focuser drawtube. You must first
loosen the two thumb screws on the 2" eyepiece adapter
to do this. Now, insert a 2" eyepiece into the focuser, and
secure it with the two thumb screws. Focus the eyepiece as
described previously.