600 -
-100 -
500 -
-200 -
0
400 -
-300 -
300 -
-400 -
200 -
-500 -
100 -
-600 -
3.
PH Measurement (cont.)
4
At 25°C the
of water has a value of 10 where we can take
that is the activity product (aH+) by
(aOH-) is equal to ion OH-, the solution is neutral and activities of H+ and OH- must be both of 10 mols / L.
If a strong acid, such as HCl, is added to water, many ions H+ are added; this should reduce the number of ions OH-. For
example: if added HCl until the OH+ activity turns 10-2 the OH- activity must turn 10-12. The hydrogen potential scale is
Established by a definition merely operational, the acid degree or activity of ions H+ will be expressed by therm "pH”
(Hydrogenionic potential).
The pH will be defined as:
"K" dissociation
(EQ-1)
pH=-log |aH+|
If the activities of ion H+ is 10-x so pH is "x".For example, at pure water @ 25°C, the hydrogen ion activity is 10-7, so the pH
Is 7 @ 25°C.An acid solution has more ions H+ then OH-.So the ions H+ activities will be bigger than 10-7, being, 10-6, 10-5
and more. The pHof an acid solution by definition, must be lower than 7, will be 6, 5, 4...
If the OH- number exceed the number of ions H+ the H+ activity must be lower than 10-7, being, 10-8, 10-9 and more... The
pHwill be bigger then 7, will be 8, 9, 10...
To avoid solution ionic concentration modification being measured it is necessary that the current that goes thru the circuitry
composed by the galvanic cell (pH electrode) be minimum (I < 1pA), such as the voltage drop caused by the internal
resistance of the same electrochemistry cell being null, not to cause measuring errors. Such condition restrict the choice to
Choose the instrument to a
"HIGH IMPEDANCE VOLTMETER”
. The instrument will have a scale graduated in pH,
calibrated by glass electrode and a reference electrode based on the relation between the pH and the electromagnetic force
Of the cell.
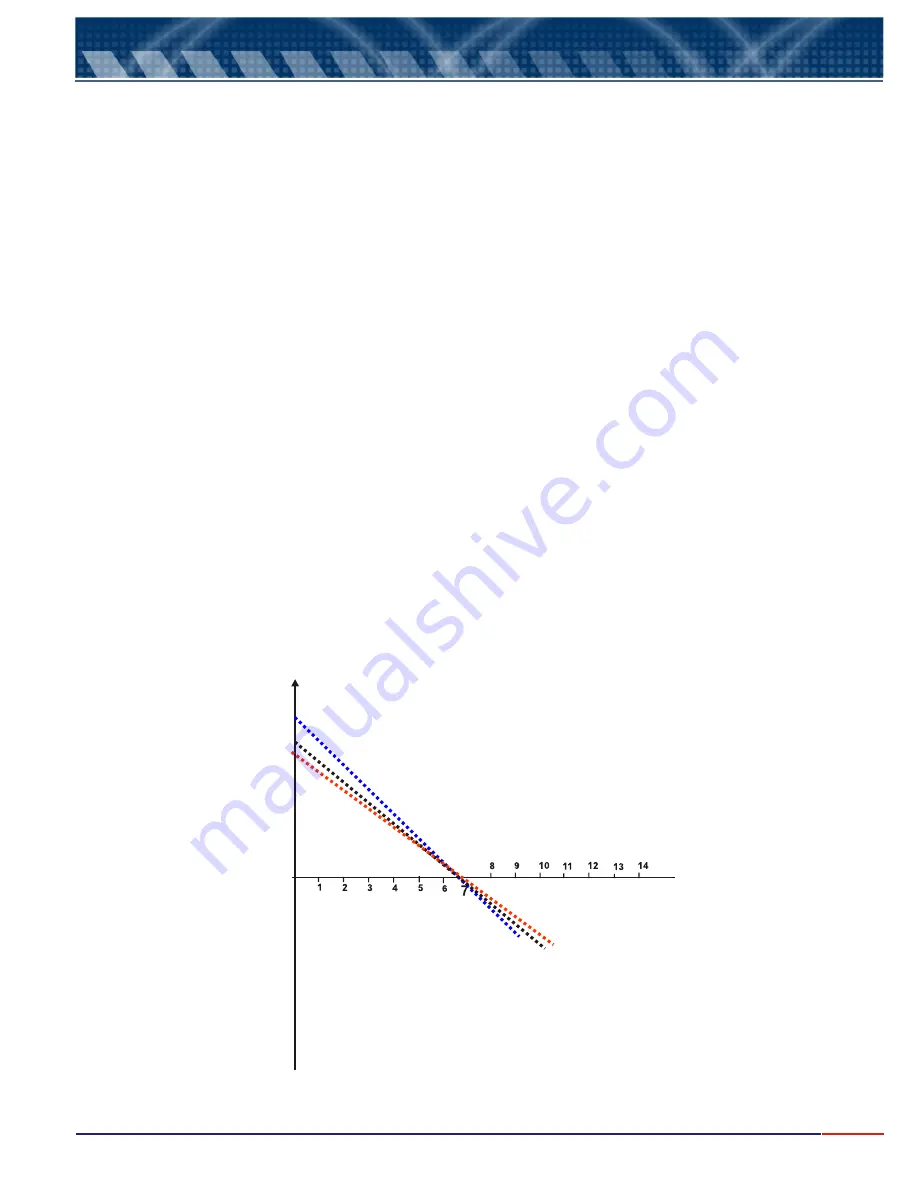
Above equation, define the equation of a line, whose decline is
and whose origin ordenate is . The electrode must
have a zero volts point (isopotential), that can be achieve performing a correspondence to 7 to zero volts, to any
temperature, using a internal BUFFER at the glass electrode, whose pH variation with the temperature compensates to the
temperature variation at the electrode.
The approximate decline of the line mV / pH involves the factor adjustment of factor KT @ 59.16 mV decade of pH, @ 25°C
by controlling the equipment “
that does the decline around the isopotential. The temperature compensator is
applied to correct the decline based on real sample temperature, varying the definition of the instrument, relating to a
1pHunit, from54.20 mV @ 0°C up to 66.10 mV @ 60°C.
-KT
E
SENSIBILITY"
E = E0 - KT (pH)
Summary of Contents for PHB21
Page 1: ...PHB21 Portable pH mV Meter...
Page 2: ......
Page 34: ...8 Maintenance 32 CLEANING CONSIDERATIONS CONSIDERATIONS...
Page 36: ...9 Communication Cable 34 E...
Page 37: ......
Page 38: ...M 4507 0908...







































