µ
PD75P308
15
4.
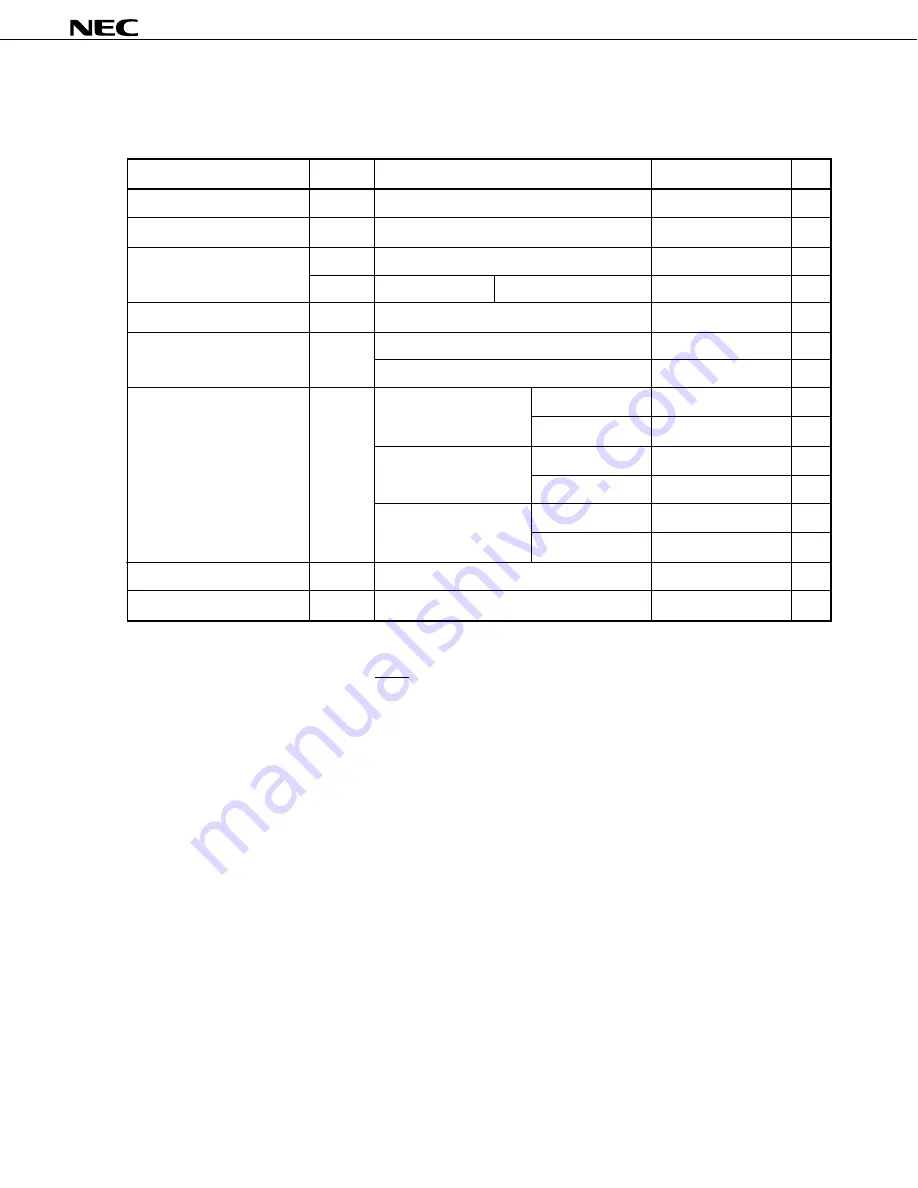
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(T
a
= 25
°
C)
Parameter
Symbol
Conditions
Rating
Unit
Supply Voltage
V
DD
-0.3 to +7.0
V
Supply Voltage
V
PP
-0.3 to +13.5
V
V
I1
Other than ports 4 or 5
-0.3 to V
DD
+0.3
V
V
I2
*1
Ports 4 and 5
Open-drain
-0.3 to +11
V
Output Voltage
V
O
-0.3 to V
DD
+0.3
V
1 Pin
-15
mA
I
OH
All pins
-30
mA
Peak value
30
mA
Effective value
15
mA
Peak value
100
mA
Effective value
60
mA
Peak value
100
mA
Effective value
60
mA
Operating Temperature
T
opt
-10 to +70
°
C
Storage Temperature
T
stg
-65 to +150
°
C
*1:
The impedance of the power source (pull-up resistor) must be 50 K
Ω
minimum when a voltage higher
than 10V is applied to ports 4 and 5.
2:
Effective value = Peak value x
√
Duty
One pin
Total of ports 0, 2, 3, 5
Total of ports 4, 6, 7
I
OH
*2
High-Level Output Current
Low-Level Output Current
Input Voltage
















































