Chapter 7
Counters
©
National Instruments Corporation
7-5
Non-Cumulative Buffered Edge Counting
Non-cumulative edge counting is similar to buffered (sample clock) edge
counting. However, the counter resets after each active edge of the Sample
Clock. You can route the Sample Clock to the Gate input of the counter.
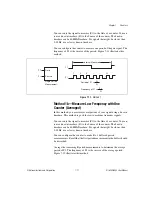
Figure 7-5 shows an example of non-cumulative buffered edge counting.
Figure 7-5.
Non-Cumulative Buffered Edge Counting
Notice that the first count interval begins when the counter is armed, which
occurs before the first active edge on Gate.
Notice that if you are using an external signal as the Source, at least one
Source pulse should occur between each active edge of the Gate signal.
This condition ensures that correct values are returned by the counter. If this
condition is not met, consider using duplicate count prevention.
Controlling the Direction of Counting
In edge counting applications, the counter can count up or down. You can
configure the counter to do the following.
•
Always count up
•
Always count down
•
Count up when the Counter
n
B input is high; count down when it is
low
For information on connecting counter signals, refer to the
2
2
3
2
3
3
Counter
Armed
SOURCE
Counter Value
1
1
0
1
3
3
1
2
2
2
Buffer
Sample Clock
(Sample on Rising Edge)