ZA-4000 User’s Manual
Appendix B. Glossary
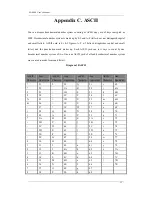
Diagram 9Glossary
Glossary
Expiation
802.11a
IEEE specification for wireless networking at 54 Mbps using
direct-sequence spread-spectrum (DSSS) technology and operating in
the unlicensed radio spectrum at 5GHz. 802.11a provides
specifications for wireless ATM systems and is used in access hubs.
Networks using 802.11a operate at radio frequencies between 5.180
GHz and 5.825 GHz. The specification uses a modulation scheme
known as orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM) that is
especially well suited to use in office settings. In 802.11a, data speeds
as high as 54 Mbps are possible.
Access Point
In a wireless local area network (WLAN), an Access Point is a station
that transmits and receives data (sometimes referred to as a
transceiver). An Access Point connects users to other users within the
network and also can serve as the point of interconnection between the
WLAN and a fixed wire network. Each Access Point can serve
multiple users within a defined network area; as people move beyond
the range of one Access Point, they are automatically handed over to
the next one. A small WLAN may only require a single Access Point;
the number required increases as a function of the number of network
users and the physical size of the network.
Infrastructure
In the infrastructure mode, the wireless access point converts airwave
data into wired Ethernet data, acting as a bridge between the wired
LAN and wireless clients. Connecting multiple Access Points via a
wired Ethernet backbone can further extend the wireless network
coverage. As a mobile computing device moves out of the range of one
access point, it moves into the range of another. As a result, wireless
- 48 -