NAL Research Corporation (TN2014-001-V1.4.5)
24
IMPORTANT:
GPS antenna should only be connected to or disconnected from the 9602-LP
when it is not powered. DO NOT CONNECT OR DISCONNECT THE GPS ANTENNA WHEN THE
9602-LP IS POWERED. The internal GPS receiver calibrates the noise-floor on power-up, and
by connecting the GPS antenna after power-up can result in prolonged acquisition time and
possibly damage the GPS receiver. To test GPS signal reacquisition, physically blocking the
signal to the antenna rather than disconnecting and reconnecting the antenna is
recommended.
IMPORTANT:
Never feed external supply voltage into the active GPS antenna. Always use
the bias voltage supplied by the 9602-LP via the SMA antenna connector to power an active
GPS antenna. Feeding voltage to the GPS antenna other than the provided bias voltage will
damage the 9602-LP.
9.0 POWER CONSUMPTION
This section gives users some insight to the electrical power profile of the 9602-LP. It does not describe
every situation and permutation possible. It should be used as a starting point for the users to continue their
own development design. The actual usage profile can vary for a number of reasons:
1.
Poor visibility of the sky where clear line of sight is not available between the 9602-LP and satellite.
2.
The higher the antenna VSWR the higher the current consumed.
3.
And manufacturing variation from device to device.
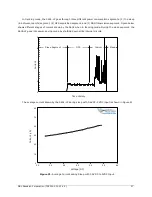
Power consumption of the 9602-LP can be divided into distinct operating segments: (1) power up, (2)
standby, (3) sleep between reports, (4) GPS acquisition, and (5) SBD report transmission. At power up in
command mode, typical in-rush current of ~3A-4A over a few milliseconds is mainly due to the current drawn
by the 9602 (see Figure 17).
Figure 16.
NAL Research’s Antenna SAF7352-IG.