OPERATING MANUAL OXYGEN MONITORING SYSTEM
OMS 420
16
7.4
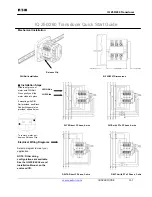
Principle of flow guidance tube
The construction of the sampling probe is using the flow guidance principle
The tube is divided in half by a metal plate welded into the middle of the tube.
The probe is mounted on the stack by means of an 8-hole flange (ANSI 4”, 150 lbs or DN100). The tip of the divider plate is ori-
ented facing towards the flow, which directs the stack gas into and through the tube at the same velocity as the flow in the stack.
The detector body is mounted on the flanged side of the tube through a hole in the flange cut for that purpose. In the body, behind
a filter screen (the measuring side of detector), the two sensors for oxygen and combustibles are exposed to the stack gas flowing
through the filter screen. In the detector behind the sensors, ambient air for reference gas diffuses through another filter screen
(for dust protection) and flushes the backside of sensors (the reference side of the detector).
Illustration for compact probe only
The flange feeds compressed air to several holes placed strategically around the detector and through a small tube, with air-
releasing orifices spaced along its entire length, which is mounted along the metal plate in the center of the probe. The timing,
duration and number of pulses of compressed air is controlled by user-settable electronic parameters and released by a solenoid
valve. During purging, compressed air blows across the filter screen protecting the sensors, and from the holes in the tiny blow-
back tube in the center of the probe, dislodging any accumulation of particulates so they will flow freely out of the probe and back
into the stack.
blowback in the stack
back-purge solenoid valve
www.
GlobalTestSupply
.com
Find Quality Products Online at: