Dowel Drill
Manual
20
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
OPERATION
ADJUSTMENT
MAINTENANCE
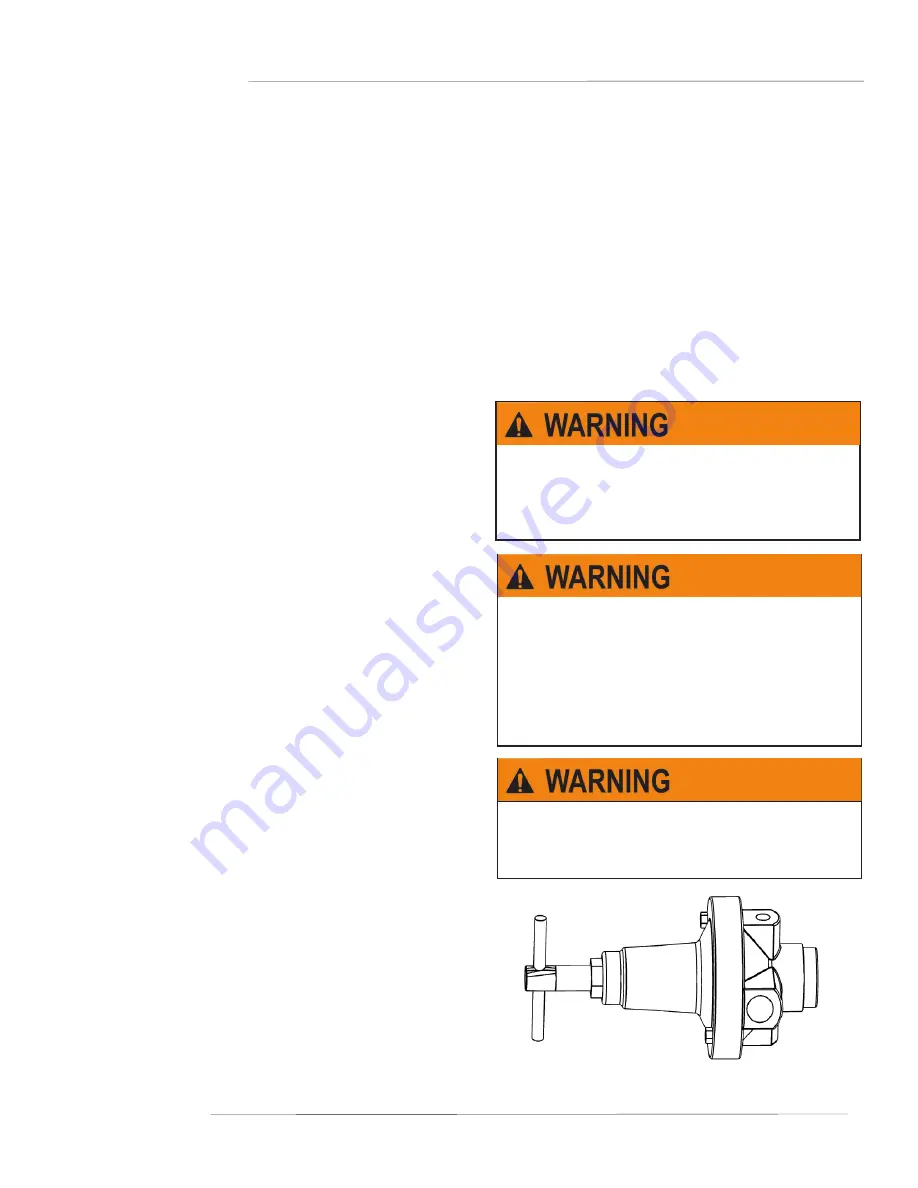
A regulator is used in a compressed air system to maintain nearly constant outlet pressure despite changes in the inlet air pressure and
changes in downstream flow requirements. Outlet pressure is controlled by the adjusting screw (1). clockwise rotation increases and
counter- clockwise rotation decreases outlet pressure setting. When the adjustment (1) is rotated fully counter- clockwise, no force is
applied to the regulating spring (2), and the valve (6) is held closed by the valve spring (7). clockwise rotation of the adjustment (1) com-
presses the regulating spring (2) which applies a downward force on top of the diaphragm (4). The diaphragm (4) and valve pin (5) move
downward forcing valve (6) off its seat (10) which allows air to flow through the regulator to the downstream system. Outlet pressure
increases in the downstream system and sensing chamber (9) and applies an upward force on bottom of the diaphragm (4). The diaphragm
(4), valve pin (5); and valve (6) move upward, compressing the regulator spring (2). Upward movement stops when the forces below the
diaphragm balance the forces above the diaphragm. When there is no downstream flow demand, the balance of forces occurs with the
valve (6) closed. When there is downstream flow demand, the balance of forces occurs when the valve opens sufficiently to compensate for
demand, thus maintaining the desired outlet pressure. RELIEVING TYPE REGULATORS. With relieving regulators, outlet pressure can be
reduced even though the system is deadended. When the adjustment (1) is turned counterclockwise, the force on the regulating spring (2)
is reduced, and air pressure in the sensing chamber (9) moves the diaphragm (4) upward. This upward movement opens the relief passage
(8) in the diaphragm and allows air to escape from the outlet side of the regulator through the relief passage (8) and vent (3) to atmosphere.
As the outlet air pressure decreases to the reduced pressure setting, the diaphragm moves downward and closes the relief passage. The
diaphragm will likewise move upward in a response to an increase in outlet pressure above the regulator setting, allowing air to escape to
the atmosphere as described above. However, the flow capacity of the relief passage is limited, and depending upon the source of the
overpressure condition, the outlet pressure might increase to a point significantly higher than the regulator setting. For this reason, the
relief feature of a regulator must not be relied upon as an overpressure safety device. See WARNING note below.
1. Before turning on system air pressure, turn regulator adjustment coun
terclockwise until all load is removed from regulating spring.
2. Turn on system air pressure.
3. Turn regulator adjustment clockwise until the desired outlet pressure is
reached.
4.To avoid minor readjustment after making a change in pressure setting,
always approach the desired pressure from a lower pressure. When
reducing from a higher to a lower setting, first reduce to some pressure
less than the desired, then bring up to the desired point.
5. Tighten jam out to lock pressure setting.
The regulator can be disassembled for servicing without removal from
pipe line. to disassemble, shut off the inlet air and reduce pressure
in inlet and outlet lines to zero. Turn adjusting screw (1) counter-
clockwise until all load is removed from regulating spring (7 or 7a):
Remove bonnet screws (4), bonnet (3), upper springrest (5), spring
(7), and diaphragm assembly (8). The intermediate springrest (6) and
compound spring (7a) are used only on 3/4” (19mm) and 1” (25.4mm)
models with 5 to 125 PSI (0.34 to 8.62 Bar) adjustment range. Un-
screw and remove bottom plug (16), O-ring (15) and valve spring (14).
Pull valve assembly (11) together with O-ring (12) out of body. Do
not remove valve seat (10) unless replacement is necessary. Remove
O-ring (9) using a hook shaped tool, taking care not to damage
O-ring seating surfaces or valve seat. Clean parts using warm water
and soap. Dry thoroughly. Inspect each part carefully. Replace any
parts which are damaged. At reassembly, apply a wipe coat of silicone
base grease to O-rings (9, 12, 15), to stem and body of valve assembly
(11), and to center bore in bottom plug (16). Apply a light even coat
of light grease to full length of threads and tip of adjusting screw (1).
Tighten valve seat (10), if previously removed, to 80-100 inch-pounds
torque (9-11.3 N-m) (1/4”, 3/8” and 1/2” sizes) (6.35mm, 9.53mm, and
12.77mm sizes) or 25-30 foot-pounds torque (33.9-40.7 N-m) (3/4” and
1” sizes) (19mm and 25.4mm sizes). Tighten bottom plug (16) snugly
by hand. Tighten bonnet screws (4) to 20-30 inch-pounds torque (2.3-
3.4 N-m) (1/4”, 3/8” and 1/2” sizes) (6.35mm, 9.53mm, and 12.77mm
sizes) or 50-60 inch-pounds torque (5.6-6.8 N-m) (3/4” and 1” sizes)
(19mm and 25.4mm sizes).
THESE REGULATORS ARE INTENDED FOR USE IN
INDUSTRIAL COMPRESSED AIR SYSTEMS ONLY.
DO NOT USE THESE REGULATORS WHERE PRES-
SURE OR TEMPERATURE CAN EXCEED RATED
OPERATING CONDITIONS. SEE SPECIFICATIONS.
IF OUTLET PRESSURES IN EXCESS OF THE REG-
ULATOR PRESSURE SETTING COULD CAUSE
DOWNSTREAM EQUIPMENT TO RUPTURE OR
MALFUNCTION, INSTALL A PRESSURE RELIEF DE-
VICE DOWNSTREAM OF THE REGULATOR. THE
RELIEF PRESSURE AND FLOW CAPACITY OF THE
RELIEF DEVICE MUST SATISFY SYSTEM REQUIRE-
MENTS.
BEFORE USING WITH FLUIDS OTHER THAN AIR,
FOR NON-INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS, OR FOR
LIFE SUPPORT SYSTEMS, CONSULT C.A. NOR-
GREN CO
MINNICH P/N 002880-00000
Summary of Contents for A-1-48
Page 22: ...Dowel Drill Manual 22 PARTS MANUAL...
Page 23: ...23 Dowel Drill Manual PARTS MANUAL...
Page 26: ...Dowel Drill Manual 26 NOTES...









































