miniDSP Ltd, Hong Kong /
/ Features and specifications subject to change without prior notice
7
2
G
ETTING
S
TARTED WITH
EARS
In a nutshell, you mount your headphones on the EARS jig
(or put your IEMs in the “ear canal”
) and run a
measurement sweep using your headphone amp and favorite measurement program. To get a useful
measurement, you will need to first load a suitable calibration/compensation file (which we provide) into the
measurement program.
2.1
A
NOTE ON MEASUREMENT CONDITIONS
Measurements should be performed under good conditions. While the sweep technique used by modern
acoustic measurement programs is quite robust, external noise can still corrupt a measurement. Be aware of
external noise sources such as computer fans, air conditioning, traffic noise, aircraft and so on. If necessary,
choose a location or time of day for measurement that minimizes noise.
Low frequencies in particular are susceptible to external noise. Even if you cannot hear (or are not aware of)
external noise sources, they can still show up in your measurements. If you are not getting consistent
measurements at low frequency, external noise is the most likely reason.
Try and keep the space around the EARS clear of other objects, and keep both sides similar
. For example, don’t
position the EARS so one channel is next to a wall and the other is facing into the room.
2.2
C
HECK THE
EARS
GAIN SETTING
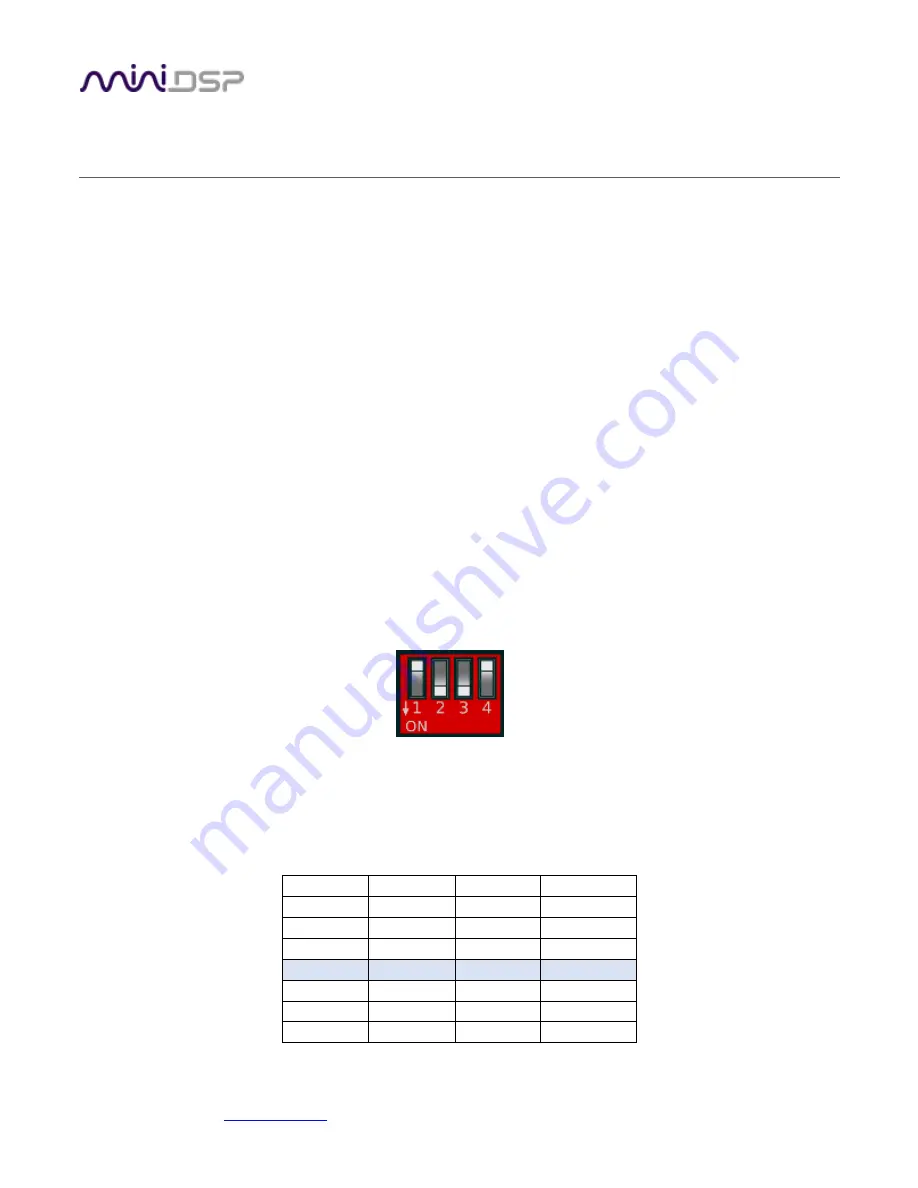
There is a bank of DIP switches on the front of the EARS.
Switches 1 to 3 control the internal gain of the microphone amplifier, as shown in Table 1. (Switch 4 is not used.)
The default gain as shipped and as indicated in the diagram above is 18 dB. The remainder of this section
assumes that the default gain is used. If you change the analog gain setting and want to display correct SPL
values, you will also need to read Measuring at higher SPLs on page 14.
Table 1. Gain switch settings
Gain (dB)
SW1
SW2
SW3
0
Down
Down
Up
6
Down
Up
Down
12
Down
Up
Up
18
Up
Down
Down
24
Up
Down
Up
30
Up
Up
Down
36
Up
Up
Up








































