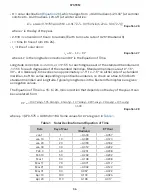
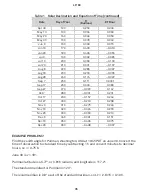
33
LP-80
relating to the interception of PAR at a given angle. In situ measurements of LAI using
hemispherical photography were equated with this new term “effective plant area index” (
L
e
),
which was defined as:
Equation 24
L
e
= Ω
L
where
L
e
represents the actual LAI (equal to a harvested leaf area measurement) and
Ω
refers to a clumping index resulting from the nonrandom distribution of canopy elements.
When a canopy displays random dispersion,
Ω
is unity; however, when a canopy is clumped,
Ω
is not unity. In a randomly dispersed canopy,
L
would be equal to
L
e
(
). In an
underdispersed canopy (clumped),
L
would be greater than
L
e
(leaves preferentially shade
the leaves). In an overdispersed canopy,
L
would be less than
L
e
(leaves are in the open
spaces).
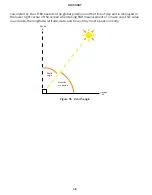
L
=
L
e
L
>
L
e
L
<
L
e
Figure 28 Diagrams showing randomly dispersed, underdispersed, and overdispersed
canopies, respectively
The purpose of this discussion is to expose the possible errors that may occur when making
LAI measurements in situ. When setting up an experiment, carefully examine the desired
end result. If the only measurement of interest is interception of PAR within a canopy, the
apparent leaf or plant area index that is calculated through inversion will be an accurate
portrayal of the canopy structure and orientation with respect to light interception. In this
instance, while clumping effects within the canopy remain present, these effects do not
cause error with regard to light interception and the effective area index for that situation.
Alternately, if obtaining the actual biomass (represented by
L
in this discussion) is desired,
all measurements should be performed to minimize the effects of clumping. The method
used in the LP-80 to compute
τ
follows the recommendation of Lang and Yueqin (1986) for
minimizing clumping effects. Measuring at certain times of day or at positions within the
canopy may also directly minimize clumping effects.
3.4.7 ZENITH ANGLE AND EQUATION OF TIME
The formulas for calculating elevation angle are relatively straightforward. The zenith angle
is calculated with
:
Equation 25
Ψ =
+
−
Lat
D
Lat
D
t t
arccos(sin
sin
cos
cos cos0.2618(
))
0
using the following definitions:
•
Lat
= the latitude (negative in the Southern Hemisphere). Latitude of a given site is easily
found in an atlas or using a GPS system.