will see that the moons are in a different
position every night. As you get better at
drawing, try more challenging sights, like a
crater system on the moon or even a nebula.
Go your library or check out the internet for
more information about astronomy. Learn
about the basics: light years, orbits, star
colors, how stars and planets are formed,
red shift, the big bang, what are the different
kinds of nebula, what are comets, asteroids
and meteors and what is a black hole. The
more you learn about astronomy, the more
fun, and the more rewarding your telescope
will become.
SOME OBSERVING TIPS
Eyepieces
: Always begin your observations
using the 25mm low-power eyepiece. The
25mm eyepiece delivers a bright, wide field
of view and is the best to use for most
viewing conditions. Use the high-power 9mm
eyepiece to view details when observing the
Moon and planets. If the image become
fuzzy, switch back down to a lower power.
Changing eyepieces changes the power or
magnification of your telescope.
By the way, you might have noticed
something strange when you looked through
your eyepiece. Although the image is right-
side up, it is reversed. That means reading
words can be a problem. But it has no affect
on astronomical objects. If you wish to have
a fully corrected image, check out Meade’s
optional Erecting Prism in the Optional
Accessory section.
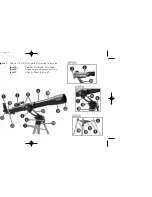
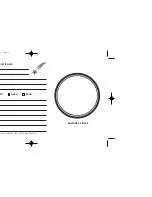
Barlow lens
: You can also change
magnification by using your Barlow. Remove
the eyepiece from the diagonal mirror and
slide in the Barlow. And then place the
eyepiece into the Barlow. Tighten the
thumbscrews to secure the Barlow lens and
the eyepiece in place. The Barlow
lens included with your telescope
doubles the power of your telescope.
See Fig. 6.
Meade offers a complete line of eyepieces
for your telescope. Most astronomers have
four or five low-power and high power
eyepieces to view different objects and to
cope with different viewing conditions.
Objects move in the eyepiece
: If you are
observing an astronomical object (the Moon,
a planet, star, etc.) you will notice that the
object will begin to move slowly through the
telescopic field of view. This movement is
caused by the rotation of the Earth and
makes an object move through the tele-
scope’s field of view. To keep astronomical
objects centered in the field, simply move
the telescope on one or both of its axes—
vertically and/or horizontally as needed—try
using the telescopes coarse and fine
adjustment controls. At higher powers,
astronomical objects will seem to move
through the field of view of the eyepiece
more rapidly.
9
Fig. 6
eyepiece
barlow
diagonal
mirror
Telestar RB-70.qxd 10/15/08 3:23 PM Page 11
Summary of Contents for TELESTAR RB-70
Page 1: ...N MANUAL fracting Telescope RB 70 M Page 1...
Page 2: ...M Page 2...
Page 15: ...or eries n a of an re 13 TY ies l nd M Page 15...
Page 17: ...ENT GOOD POOR DRAWING OF IMAGE SAVE ORIGINAL BE SURE TO MAKE COPIES RVATION LOG M Page 17...
Page 18: ...ENT GOOD POOR DRAWING OF IMAGE RVATION LOG M Page 18...
Page 19: ...M Page 19...