z
14
Chapter 4: OBSERVING
CHAPTER
4
OBJECTS IN SPACE
Listed below are some of the many astronomical objects that can
be seen with either ETX model telescope.
The Moon
The Moon is, on average, 239,000 miles (380,000km) from Earth.
It is best observed during its crescent or half phase, when
sunlight strikes its surface at an angle, casting shadows and
adding depth to the view (Fig. 18).
No shadows are seen during a full Moon, causing the overly
bright Moon to appear flat and uninteresting through the
telescope. Using either ETX model, brilliant detail can be
observed on the Moon, including hundreds of lunar craters and
maria, described below.
Craters are round meteor impact sites covering most of the
Moon’s surface. With no atmosphere on the Moon, no weather
conditions exist, so the only erosive force is meteor strikes. Under
these conditions, lunar craters can last for millions of years.
Maria (plural for mare, seas) are smooth, dark areas scattered
across the lunar surface. These areas are ancient impact basins
that were filled with lava from the interior of the Moon by the depth
and force of the meteor or comet impact.
12 Apollo astronauts left their bootprints on the Moon in the late
1960’s and early 1970’s. However, no telescope on Earth can see
these footprints or any other artifacts. In fact, the smallest lunar
features that may be seen with the largest telescope on Earth are
about one-half mile across.
NOTE:Except during its early or late crescent phases, the Moon
can be an exceptionally bright object to view through the
telescope. To reduce the brightness and glare, use the #905
Variable Polarizing Filter (see OPTIONAL ACCESSORIES, page18).
Planets
Planets change positions in the sky as they orbit around the Sun.
To locate the planets on a given day or month, consult a monthly
astronomy magazine, such as Sky and Telescope or Astronomy.
Listed below are the best planets for viewing through either ETX
model telescope.
Venus is about nine-tenths the diameter of Earth. As Venus orbits
the Sun, observers can see it go through phases (crescent, half,
and full) much like those of the Moon. The disk of Venus appears
white, as sunlight is reflected off the thick cloud cover that
completely obscures any surface detail.
Mars is about half the diameter of Earth. Through the telescope
it appears as a tiny reddish-orange disk. You may see a hint of
white at one of the planet’s polar ice caps. Approximately every
two years, when Mars is closest to Earth, additional detail and
coloring on the planet's surface may be visible.
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, with a diameter
11 times that of Earth. Jupiter appears as a disk with dark lines
stretching across the surface. These lines are cloud bands in the
atmosphere. Four of Jupiter’s 16 moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede,
and Callisto) can be seen as star-like points of light when you use
even the lowest magnification. The number of moons visible on
any given night changes as they circle around the giant planet.
Saturn is nine times the diameter of Earth and appears as a
small, round disk with rings extending out from either side. In
1610, Galileo, the first person to observe Saturn through a
telescope, did not understand that what he was seeing were
rings. Instead, he believed that Saturn had “ears.” Saturn’s rings
are composed of billions of ice particles, ranging in size from a
speck of dust to the size of a house. The major division in
Saturn's rings, called the Cassini Division, is generally visible
through both ETX models. Titan, the largest of Saturn’s 18 moons
can also be seen as a bright, star-like object near the planet.
Deep-Sky Objects
You can use star charts to locate constellations, individual stars,
and deep-sky objects. Examples of various deep-sky objects are
given below:
Stars are large gaseous objects that are illuminated by nuclear
fusion in their core. Because of their vast distances from our solar
system, all stars appear as pinpoints of light, regardless of the
size of the telescope used.
Nebulae are vast interstellar clouds of gas and dust where stars
are formed. Most impressive of these is the Great Nebula in Orion
(M42), a diffuse nebula that appears as a faint wispy gray cloud.
M42 is 1600 light years from Earth.
Open Clusters are loose groupings of young stars, all recently
formed from the same diffuse nebula. The Pleiades (Fig. 19) is an
open cluster 410 light years from Earth. Several hundred stars of
the cluster are visible through both ETX models .
Constellations are large, imaginary patterns of stars believed by
ancient civilizations to be the celestial equivalent of objects,
animals, people, or gods. These patterns are too large to be seen
through a telescope. To learn the constellations, start with an
easy grouping of stars, such as the Big Dipper in Ursa Major.
Then use a star chart to explore across the sky.
Galaxies are large assemblies of stars, nebulae, and star
clusters that are bound by gravity. The most common shape is
spiral (such as our own Milky Way), but galaxies can also be
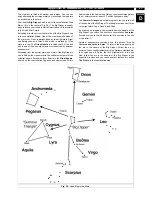
elliptical, or even irregular blobs. The Andromeda Galaxy (M31)
is the closest spiral-type galaxy to our own. This galaxy appears
fuzzy and cigar-shaped. It is 2.2 million light years away in the
constellation Andromeda, located between the large “W” o f
Cassiopeia and the great square of Pegasus. Under clear, dark
conditions, M31 can be seen with the naked eye and is a
fascinating object through both ETX models.
Fig. 18: This photo of the Moon shows the rich detail afforded
by shadows.
Fig. 19: The Pleiades Star Cluster (M45) in the constellation
Taurus.