10 ENGLISH
Overload protection
When the tool or battery is operated in a manner that
causes it to draw an abnormally high current, the tool
automatically stops without any indication. In this sit-
uation, turn the tool off and stop the application that
caused the tool to become overloaded. Then turn the
tool on to restart.
Overheat protection
When the tool or battery is overheated, the tool stops
automatically and the lamp blinks. In this case, let the
tool and battery cool before turning the tool on again.
Overdischarge protection
When the battery capacity is not enough, the tool stops
automatically. If you turn the tool on, the motor runs
again but stops soon. In this case, remove the battery
from the tool and charge the battery.
Protections against other causes
Protection system is also designed for other causes
that could damage the tool and allows the tool to stop
automatically. Take all the following steps to clear the
causes, when the tool has been brought to a temporary
halt or stop in operation.
1. Turn the tool off, and then turn it on again to
restart.
2. Charge the battery(ies) or replace it/them with
recharged battery(ies).
3. Let the tool and battery(ies) cool down.
If no improvement can be found by restoring protection
system, then contact your local Makita Service Center.
Indicating the remaining battery
capacity
Only for battery cartridges with the indicator
►
Fig.2:
1.
Indicator lamps
2.
Check button
Press the check button on the battery cartridge to indi
-
cate the remaining battery capacity. The indicator lamps
light up for a few seconds.
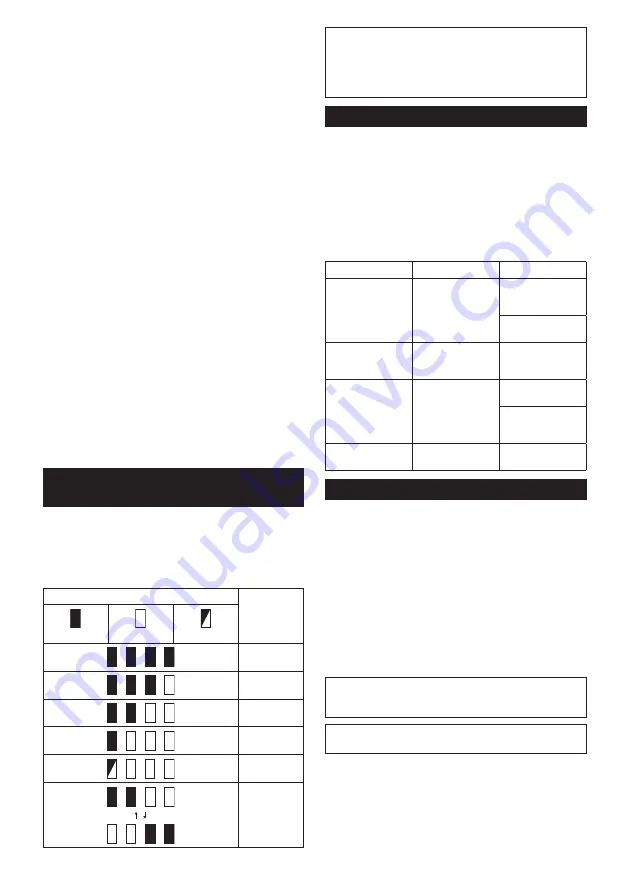
Indicator lamps
Remaining
capacity
Lighted
Off
Blinking
75% to 100%
50% to 75%
25% to 50%
0% to 25%
Charge the
battery.
The battery
may have
malfunctioned.
NOTE:
Depending on the conditions of use and the
ambient temperature, the indication may differ slightly
from the actual capacity.
NOTE:
The first (far left) indicator lamp will blink when
the battery protection system works.
Selecting the cutting action
►
Fig.3:
1.
Cutting action changing lever
This tool can be operated with an orbital or a straight
line (up and down) cutting action. The orbital cutting
action thrusts the jig saw blade forward on the cutting
stroke and greatly increases cutting speed.
To change the cutting action, just turn the cutting action
changing lever to the desired cutting action position.
Refer to the table to select the appropriate cutting
action.
Position
Cutting action
Applications
0
Straight line cutting
action
For cutting mild
steel, stainless
steel and plastics.
For clean cuts in
wood and plywood.
I
Small orbital
cutting action
For cutting mild
steel, aluminum
and hard wood.
II
Medium orbital
cutting action
For cutting wood
and plywood.
For fast cutting in
aluminum and mild
steel.
III
Large orbital
cutting action
For fast cutting in
wood and plywood.
Switch action
To turn on the tool, press the lock/unlock button. The
tool turns into the standby mode. To start the tool, pull
the switch trigger in the standby mode. Tool speed is
increased by increasing pressure on the switch trigger.
To stop the tool, release the switch trigger. The tool
turns into the standby mode. To turn off the tool, press
the lock/unlock button in the standby mode.
For continuous operation, pull the switch trigger in the
standby mode, and then push in the lock on button.
To stop the tool, pull the switch trigger fully, and then
release it.
►
Fig.4:
1.
Lock/unlock button
2.
Lock on button
3.
Switch trigger
NOTE:
If the tool is left for 10 seconds without any
operation in the standby mode, the tool automatically
turns off and the lamp goes off.
NOTE:
The lock/unlock button is not available while
the tool is operating.
Summary of Contents for DJV184RFJ
Page 2: ...2 1 2 3 Fig 1 1 2 Fig 2 1 Fig 3 1 2 3 Fig 4 1 Fig 5 1 Fig 6 1 3 2 Fig 7 ...
Page 3: ...3 1 2 3 Fig 8 1 2 3 Fig 9 1 Fig 10 2 1 Fig 11 Fig 12 3 2 1 Fig 13 2 1 Fig 14 ...
Page 4: ...4 3 2 1 Fig 15 Fig 16 Fig 17 Fig 18 1 Fig 19 1 Fig 20 ...
Page 5: ...5 1 Fig 21 1 2 Fig 22 Fig 23 1 Fig 24 1 2 4 3 Fig 25 1 Fig 26 2 6 5 4 1 3 Fig 27 1 2 Fig 28 ...
Page 6: ...6 1 2 Fig 29 1 2 3 Fig 30 3 2 1 Fig 31 ...
Page 90: ...90 ...
Page 91: ...91 ...











































