11 ENGLISH
Dust extraction
The dust nozzle (optional accessory) is recommended
to perform clean cutting operations.
►
Fig.12:
1.
Dust nozzle
2.
Base
To attach the dust nozzle on the tool, insert the hook of
dust nozzle into the hole in the base.
►
Fig.13:
1.
Clamp screw
To secure the dust nozzle, tighten the clamp screw at
the front of the dust nozzle.
The dust nozzle can be installed on either left or right
side of the base.
►
Fig.14:
1.
Dust nozzle
2.
Hose for vacuum cleaner
Then connect a Makita vacuum cleaner to the dust
nozzle.
OPERATION
CAUTION:
•
Always hold the base flush with the workpiece.
Failure to do so may cause blade breakage,
resulting in a serious injury.
NOTE:
•
If the tool is operated continuously until the
battery cartridge has discharged, allow the tool
to rest for 15 minutes before proceeding with a
fresh battery.
►
Fig.15:
1.
Cutting line
2.
Base
Turn the tool on without the blade making any contact
and wait until the blade attains full speed. Then rest
the base flat on the workpiece and gently move the tool
forward along the previously marked cutting line.
When cutting curves, advance the tool very slowly.
Bevel cutting
CAUTION:
•
Always be sure that the tool is switched off and
the battery cartridge is removed before tilting
the base.
►
Fig.16
With the base tilted, you can make bevel cuts at any
angle between 0° and 45° (left or right).
►
Fig.17:
1.
Base
2.
Hex wrench
3.
Bolt
To tilt the base, loosen the bolt on the back of the base
with the hex wrench. Move the base so that the bolt is
positioned in the center of the bevel slot in the base.
►
Fig.18:
1.
Bevel slot
2.
Base
3.
Bolt
4.
Graduations
5.
V-notch
6.
Gear housing
Tilt the base until the desired bevel angle is obtained.
The V-notch of the gear housing indicates the bevel
angle by graduations. Then tighten the bolt firmly to
secure the base.
Front flush cuts
►
Fig.19:
1.
Base
2.
Hex wrench
3.
Bolt
Loosen the bolt on the back of the base with the hex
wrench and slide the base all the way back. Then
tighten the bolt to secure the base.
Cutouts
Cutouts can be made with either of two methods A or B.
A) Boring a starting hole:
►
Fig.20:
1.
Starting hole
•
For internal cutouts without a lead-in cut from an
edge, pre-drill a starting hole 12 mm or more in
diameter. Insert the blade into this hole to start
your cut.
B) Plunge cutting:
►
Fig.21
•
You need not bore a starting hole or make a
lead-in cut if you carefully do as follows.
1. Tilt the tool up on the front edge of the base with
the blade point positioned just above the work
-
piece surface.
2. Apply pressure to the tool so that the front edge of
the base will not move when you switch on the tool
and gently lower the back end of the tool slowly.
3. As the blade pierces the workpiece, slowly lower
the base of the tool down onto the workpiece
surface.
4.
Complete the cut in the normal manner.
Finishing edges
►
Fig.22
To trim edges or make dimensional adjustments, run the
blade lightly along the cut edges.
Metal cutting
Always use a suitable coolant (cutting oil) when cutting
metal. Failure to do so will cause significant blade wear.
The underside of the workpiece can be greased instead
of using a coolant.
Rip fence set (optional accessory)
CAUTION:
•
Always be sure that the tool is switched off and
the battery cartridge is removed before installing
or removing accessories.
1. Straight cuts
►
Fig.23:
1.
Rip fence
When repeatedly cutting widths of 160 mm or less, use
of the rip fence will assure fast, clean, straight cuts.
►
Fig.24:
1.
Hex wrench
2.
Bolt
3.
Fence guide
To install, insert the rip fence into the rectangular hole
on the side of the tool base with the fence guide facing
down. Slide the rip fence to the desired cutting width
position, then tighten the bolt to secure it.
Summary of Contents for 0088381651882
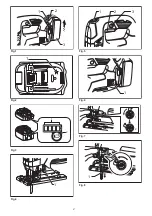
Page 2: ...1 2 3 1 1 2 1 1 2 3 1 1 2 Fig 7 1 Fig 1 Fig 2 Fig 3 Fig 4 Fig 5 Fig 6 Fig 8 2 ...
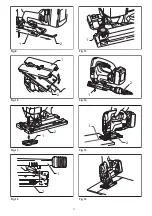
Page 3: ...1 2 1 2 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 1 2 Fig 9 Fig 10 Fig 11 Fig 12 Fig 13 Fig 14 Fig 15 Fig 16 3 ...
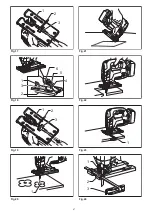
Page 4: ...1 2 3 1 2 3 4 5 6 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 3 Fig 17 Fig 18 Fig 19 Fig 20 Fig 21 Fig 22 Fig 23 Fig 24 4 ...
Page 5: ...1 2 3 1 2 1 2 3 Fig 25 Fig 26 Fig 27 Fig 28 Fig 29 5 ...
Page 66: ...66 ...
Page 67: ...67 ...