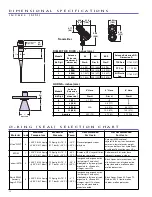
A P P L I C A T I O N S
P U L S E B U R S T R A D A R
C H A M B E R S A N D B Y P A S S
M I X E R S A N D B L E N D I N G V E S S E L S
CONDITIONS –
Turbulence, Foam, and Changing Dielectric
P R O B L E M A T I C A P P L I C A T I O N S
G U I D E D W A V E R A D A R A L T E R N A T I V E
Some applications can be problematic for Non-Contact
Radar. The following are examples of when Guided
Wave Radar is recommended.
•
Extremely low dielectric media (
ε
r<1.7)
•
Very weak reflections from the liquid surface
(particularly during turbulence) can cause poor
performance.
•
Tanks heavily cluttered with false targets (mixers,
pumps, ladders, pipes, etc.)
•
During times of very low liquid levels of low dielec-
tric media, the metal tank bottom may be detected,
which can deteriorate performance.
•
Foam can either absorb or reflect the microwave
energy depending upon the depth, dielectric, density
and wall thickness of the bubbles. Due to typical
variations in the amount (depth) of foam, it is
impossible to quantify performance. It may be
possible to receive most, some or none of the
transmitted energy.
•
Extremely high liquid level (Overflow) conditions
when liquid very near the antenna can cause
erroneous readings and measurement failure.
Refer to ECLIPSE Model 706 Guided Wave Radar
bulletin 57-106.
8