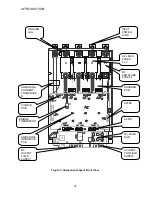
INSTALLATION
24
Installation
Pre-Installation Considerations
Receipt of Shipment
All equipment is tested against defect at the
factory. Any damages or shortages evident
when the equipment is received must be
reported immediately to the commercial
carrier who transported the equipment.
Assistance, if required, is available from your
Magnetek representative. Always refer to the
order number, equipment description, and
serial number when contacting Magnetek.
Unpacking Instructions
Remove the protective shipping material from
around the equipment. Remove all packing
material. Unbolt the equipment from its crate.
Inspect for loose wiring. Make sure that all
contact wedges and other shipping devices
have been removed.
Packing Instructions for Reshipment
or Storage
For long periods of storage, equipment should
be covered to prevent corrosion and should
be placed in a clean, dry, location. If possible,
equipment should be stored in its original
crating. Periodic inspection should be made
to ensure that the equipment is dry and that
no condensation has accumulated. The
equipment warranty does not cover damage
due to improper storage.
The drive should be packed in its original
shipping container if it is required that it be
shipped. Assistance, if required, is available
from your Magnetek representative.
Physical Installation
The DSD 412 Elevator Drive is air-cooled.
The lowest HP rated units are cooled by
convection; all other units are equipped with a
fan to ensure adequate airflow. Select a site
for installing the drive that is clean and well
ventilated. Maintenance will be minimized if
the drive is located in a clean atmosphere.
The standard drive is designed for vertical
mounting. Attach the drive to a cabinet panel
or other vertical structure using the mounting
holes provided at the back of the drive.
Ensure that the unit is level.
Selecting, Mounting and Wiring of the
Digital Encoder
Encoder Selection
A quality encoder is recommended for use
with the DSD 412 controller for speed
feedback. The encoder should be a two
channel, quadrature, zero speed type device
with differential line drivers. The DSD 412
drive su5V power for an encoder,
however the encoder and feedback signals
may operate from another source, up to 15
volts if desired. The Pulses per Revolution
count must be sufficient to provide an
adequate frequency feedback at very low
speeds, and yet not exceed 300 kHz (per
channel) at top speed. For most elevator
applications this target will be met when the
feedback frequency (per channel) is greater
than 50KHz at contract speed. For gearless
machines, which have a base speed around
100RPM, a 10,000PPR encoder is a good
choice for direct connection to the motor shaft.
For geared machines, with motors running at
1750 or 1150RPM, 2500PPR encoder may be
used. Direct mounted hollow shaft encoders,
electrically insulated from motor shaft and
motor frame will yield the best results. The
use of an analog AC or DC tachometer is not
supported by DSD 412 elevator drives
software or hardware.
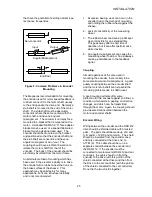
Mounting
Proper mounting and alignment of the digital
encoder used for speed feedback is very
critical for the smooth operation of the DSD
412 controller. Even the slightest wobble of
the encoder shaft due to misalignment can
cause once-per-revolution torque pulsation
Summary of Contents for DSD 412
Page 1: ...DSD 412 DC Elevator Drive Technical Manual CS00407 rev 06...
Page 6: ...6...
Page 102: ...MAINTENANCE 102 Figure 24 Connector and E prom Locations...
Page 103: ...MAINTENANCE 103 Figure 25 Test Point Locations...
Page 115: ...OUTLINE DRAWING 100A 115 Figure 26 Drive Chassis Outline DSD 412 100 Amp...
Page 116: ...OUTLINE DRAWING 190A 116 Figure 27 Drive Chassis Outline DSD 412 195 Amp...
Page 117: ...OUTLINE DRAWING 300A 117 Figure 28 Drive Chasis Outline DSD 412 300 Amp...
Page 118: ...LAYOUT DRAWING 100A 118 Figure 29 Layout DSD 412 100 Amp A3 A1 A2 A2 L1 NEG GND L2 L3 POS...
Page 119: ...LAYOUT DRAWING 195A 119 Figure 30 Layout DSD 412 195 Amp A3 A1 A2 A2...
Page 120: ...LAYOUT DRAWING 300A 120 Figure 31 Layout DSD 412 300 Amp A3 A1 A2 A2...
Page 121: ......