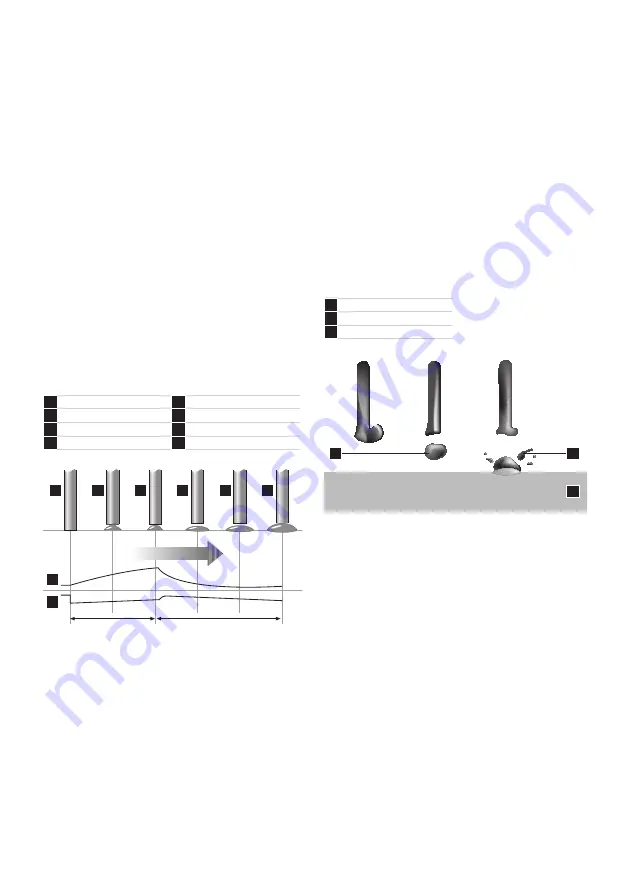
10
and arc voltage settings cause the electrode to
intermittently short-circuit with the weld pool
at a controlled frequency. Metal is transferred
by the wire tip actually dipping into the weld
pool and the short-circuit current is sufficient
to allow the arc to be re-established. This short-
circuiting mode of metal transfer effectively
extends the range of MIG welding to lower
currents so thin sheet material can readily
be welded. The low heat input makes this
technique well-suited to the positional welding
of root runs on thick plate, butt welds for
bridging over large gaps and for certain difficult
materials where heat input is critical. Each
short-circuit causes the current to rise and the
metal fuses off the end of the electrode. A high
short-circuiting frequency gives low heat input.
Dip transfer occurs between ±70-220A, 14–23
arc volts. It is achieved using shielding gases
based on carbon dioxide and argon.
1
Short circuit
5
Arc gap shortens
2
Necking
6
Short circuit
3
Arc re-ignition
7
Current (A)
4
Arc established
8
Voltage (V)
1
2
6
3
4
5
Time
Short circuit cycle
Arcing cycle
7
8
Schematic of Dip Transfer
Metal-cored wires transfer metal in dip mode
at low currents just like solid MIG wires. This
transfer mode is used for all positional work
with these types of wire.
Globular Transfer
Metal transfer is controlled by slow ejection
resulting in large, irregularly-shaped ‘globs’
falling into the weld pool under the action of
gravity. Carbon dioxide gas drops are dispersed
haphazardly. With argon-based gases, the
drops are not as large and are transferred
in a more axial direction. There is a lot of
spatter, especially in carbon dioxide, resulting
in greater wire consumption, poor penetration
and poor appearance. Globular transfer occurs
between the dip and spray ranges. This mode
of transfer is not recommended for normal
welding applications and may be corrected
when encountered by either decreasing the arc
voltage or increasing the amperage. Globular
transfer can take place with any electrode
diameter.
1
Large droplet
2
Splatter
3
Workpiece
1
2
3
Schematic of Globular Transfer
Basic flux-cored wires tend to operate in a
globular mode or in a globular-spray transfer
mode where larger than normal spray droplets
are propelled across the arc, but they never
achieve a true spray transfer mode. This transfer
mode is sometimes referred to as non-axial
globular transfer.
Self-shielded flux-cored wires operate in a
predominantly globular transfer mode although
at high currents the wire often ‘explodes’
across the arc.
Spray Transfer
In spray transfer, metal is projected by an
electromagnetic force from the wire tip in
the form of a continuous stream of discrete
droplets approximately the same size as the
























