For Position PID
●
Position Target (in [rad])
●
kP (proportional gain)
●
kI (integral gain)
●
kD (derivative gain)
●
I windup (maximal output of an integral part in [rad/s])
●
Max output (in [rad/s])
For Velocity PID:
●
Velocity Target (in [rad/s])
●
kP (proportional gain)
●
kI (integral gain)
●
kD (derivative gain)
●
I windup (maximal output of an integral part in[Nm])
●
Max output (in [Nm])
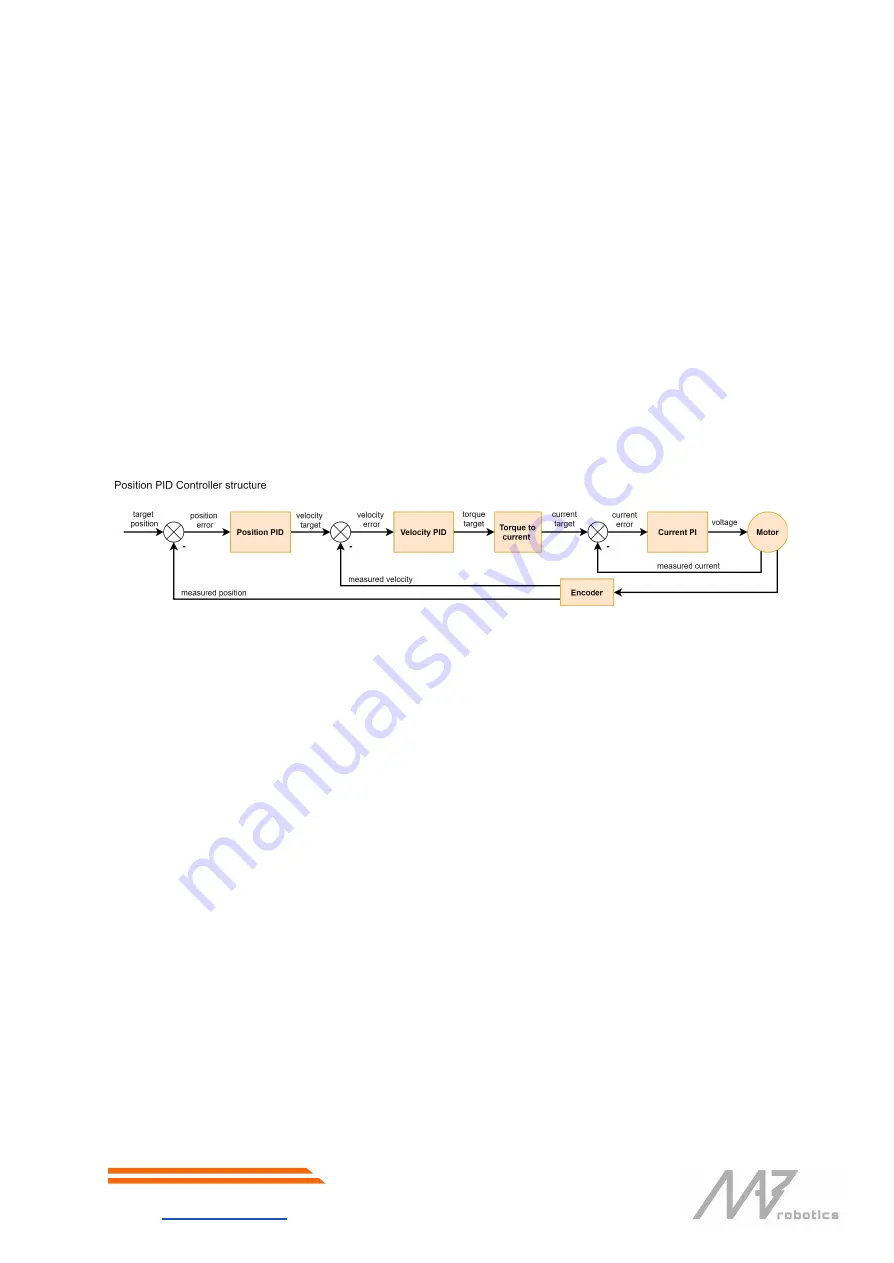
To properly tune the controller, it is recommended to first tune the velocity controller (in Velocity PID mode),
and then the Position PID. The controller can be described with a diagram:
Impedance PD
Impedance Control mode is a popular choice for mobile or legged robots, as well as for any compliant
mechanism. The main idea behind it is to mimic the behavior of a torsional spring with variable stiffness and
damping. The parameters of the controller are:
●
Position Target
●
Velocity Target
●
kP (position gain)
●
kD (velocity gain)
●
Torque Feed Forward (Torque FF)
The torque output is proportional to the position error and velocity error and additionally supplemented
with a torque command from the user. Here are some of the most common applications for this control
mode:
●
Spring-damper mechanism
- when Velocity Target is set to 0, Impedance Controllers kP gain acts
as the virtual spring stiffness and kD as its damping coefficient.
Example use case: a variable suspension for a wheeled robot, where suspension stiffness can be
regulated by kP, damping by kD, and height (clearance) by changing the Target Position;
●
High-frequency torque controller
, where its Targets and Gains can act as stabilizing agents to the
torque command.
Example use case: In legged robots, force control can be achieved by advanced control algorithms,
which usually operate at rates below 100 Hz. It is usually enough to stabilize the robot but too slow
to avoid vibrations. Knowing desired robot's joint positions, velocities, and torques, drives can be
set to produce the proper torque and hold the position/velocity with small gains. This would
www.mabrobotics.pl








































