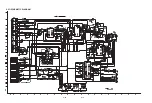
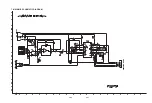
1-4
ESD PRECAUTIONS
Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESD)
Some semiconductor (solid state) devices can be damaged easily by static electricity. Such components
commonly are called Electrostatically Sensitive Devices (ESD). Examples of typical ESD devices are integrated
circuits and some field-effect transistors and semiconductor chip components. The following techniques should
be used to help reduce the incidence of component damage caused by static electricity.
1. Immediately before handling any semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly, drain off
any electrostatic charge on your body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, obtain and wear a
commercially available discharging wrist strap device, which should be removed for potential shock reasons
prior to applying power to the unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ESD devices, place the assembly on a conductive surface
such as aluminum foil, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup or exposure of the assembly.
3. Use only a grounded-tip soldering iron to solder or unsolder ESD devices.
4. Use only an anti-static solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as "anti-static" can
generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ESD devices.
5. Do not use freon-propelled chemicals. These can generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ESD
devices.
6. Do not remove a replacement ESD device from its protective package until immediately before you are
ready to install it. (Most replacement ESD devices are packaged with leads electrically shorted together by
conductive foam, aluminum foil or comparable conductive materials).
7. Immediately before removing the protective material from the leads of a replacement ESD device, touch the
protective material to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will by installed.
CAUTION : BE SURE NO POWER IS APPLIED TO THE CHASSIS OR CIRCUIT, AND OBSERVE ALL OTHER
SAFETY PRECAUTIONS.
8. Minimize bodily motions when handing unpackaged replacement ESD devices. (Otherwise harmless motion
such as the brushing together of your clothes fabric or the lifting of your foot from a carpeted floor can gener-
ate static electricity sufficient to damage an ESD device).
CAUTION. GRAPHIC SYMBOLS
THE LIGHTNING FLASH WITH APROWHEAD SYMBOL. WITHIN AN EQUILATERAL TRIANGLE, IS
INTENDED TO ALERT THE SERVICE PERSONNEL TO THE PRESENCE OF UNINSULATED
“DANGEROUS VOLTAGE” THAT MAY BE OF SUFFICIENT MAGNITUDE TO CONSTITUTE A RISK OF
ELECTRIC SHOCK.
THE EXCLAMATION POINT WITHIN AN EQUILATERAL TRIANGLE IS INTENDED TO ALERT THE
SERVICE PERSONNEL TO THE PRESENCE OF IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION IN SERVICE
LITERATURE.
Summary of Contents for ACC75T
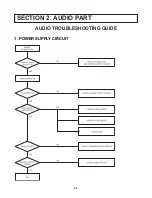
Page 7: ...2 1 SECTION 2 AUDIO PART AUDIO TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE 1 POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT ...
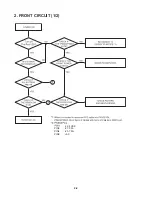
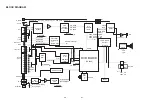
Page 8: ...2 2 2 FRONT CIRCUIT 1 2 PIN3 PIN4 PIN9 27 5 FL 32 4 VKK 23 7 FL 5 0 CN902 CN902 ...
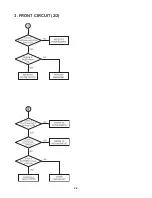
Page 9: ...2 3 3 FRONT CIRCUIT 2 2 ...
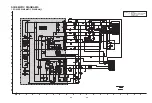
Page 13: ...2 10 2 11 2 POWER SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM_2 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T ...
Page 14: ...2 12 2 13 3 MICOM SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T ...
Page 15: ...2 14 2 15 4 FRONT SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T ...
Page 16: ...2 16 2 17 5 DSP AMP SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T ...
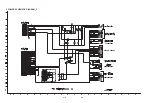
Page 17: ...2 18 2 19 6 I O SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T ...
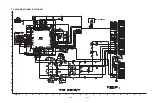
Page 18: ...2 20 2 21 7 MAIN MIC SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T ...
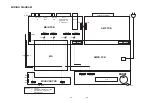
Page 19: ...2 22 2 23 PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD DIAGRAMS 1 MAIN DVD P C BOARD DIAGRAM TOP VIEW ...
Page 20: ...2 24 2 25 2 MAIN DVD P C BOARD DIAGRAM BOTTOM VIEW ...
Page 21: ...2 26 2 27 3 FRONT MIC P C BOARD 6870R7507AA ...
Page 23: ...2 30 2 31 6 AMP P C BOARD TOP VIEW BOTTOM VIEW ...
Page 26: ...3 3 A 115 ...
Page 27: ...3 4 B 1 2 ...
Page 28: ...3 5 C ES6698 ES6698 ES6698 ...
Page 29: ...3 6 D ...
Page 45: ......
Page 47: ...A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T 3 24 3 25 2 RF SERVO SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM ...
Page 48: ...3 FRONT MIC SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T 3 26 3 27 ...
Page 49: ...3 28 3 29 4 USB CONTROLLER SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T ...
Page 50: ...5 AMP SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM 5TOOL A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T 3 30 3 31 ...
Page 51: ...6 AMP SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM 7TOOL A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T 3 32 3 33 ...
Page 55: ......
Page 59: ...5 6 SUB WOOFER SPEAKER MODEL LHS 75ATW 953 954 961 950 952 955 951 956 957 A900 ...
Page 60: ...5 7 TRANSMITTER MODEL ACC75T 380 382 384 With LENS A80M A300 A80S 480 ...
Page 64: ...5 11 WIRElESS PART 4 SMPS P C BOARD DIAGRAM LOCATION GUIDE ...
Page 65: ...5 12 WIRElESS PART 5 TX P C BOARD DIAGRAM TOP VIEW BOTTOM VIEW ...
Page 66: ...5 13 WIRElESS PART 6 RX P C BOARD DIAGRAM TOP VIEW BOTTOM VIEW ...