User Manual for PuraLev
®
2000SU
www.levitronix.com
PL-4034-00, Rev02, DCO# 20-144
19
3.5 Hydraulic Circuit Design
Following general design rules help to operate the pump system optimally considering efficiency, optimum
priming behavior and low shear forces:
1.
The general rule for minimum shear forces and optimum priming behavior is to minimize the
pressure drop in the inlet circuit and avoid negative pressure at the inlet of the pump head.
2.
Minimize tubing length at the inlet of the pump head and maximize the ID
(not lower than 1” is
recommended). This reduces the pressure drop and the tendency of cavitation.
3.
Avoid any restrictions, valves, elbows, bended tubing and sharp edges at the inlet circuit of the
pump head, which potentially cause cavitation resulting in higher shear forces and bubble
collection in the pump head with the danger of priming loss.
4.
Choose correctly aligned sealing rings and fitting adaptors to connect tubing to the in- and outlet of
the pump head. Consult the dimension drawings of the sealing ring and fitting adaptor
manufacturer and check with the in- and outlet dimensions shown in
. Miss-aligned sealing
rings and fittings can be the cause of increased shear forces and cavitation effects.
5.
Place the pump at the lowest point of the hydraulic circuit. Optimum is as much as possible below a
tank or reservoir. This optimizes priming behavior and keeps the inlet pressure positive for low
shear forces.
6.
Keep the liquid level in the reservoir tank or bag as high as possible, which increases the inlet
pressure of the pump head and minimized heat up of the liquid.
7.
The optimum outlet angle of the pump head is 45 degree (see
) hence allowing gas
bubbles to leave the pump head and keep it primed.
8.
To minimize heat up of the liquid the overall pressure drop in the hydraulic circuit shall be reduced
as much as possible.
9.
It shall be avoided to pump longer times against a closed valve, which can cause heat-up of the
liquid and higher shear forces.
10.
At higher liquid temperature, the rules mentioned above, become more important due to higher
cavitation tendency of the liquid.
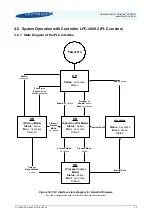
11.
Load and stress at the inlet and outlet by heavy tubing and inexact mounting alignment shall be
avoided (see
) as this can cause leakage issues due to distortion of the plastic pump
housing.
Figure 21: Avoidance of stress forces and torques at the inlet and outlet of the pump head
Contact the
Levitronix
®
Technical Service
department (see
Section 7
) for more detailed considerations and
support on the design of the hydraulic circuit.
Force/torque stress
at the in- and outlet
of the pump housing!
Tubing fixation/support to avoid
load at in- and outlet of pump system.
Pump
Heavy tubing at
in- and outlet of pump