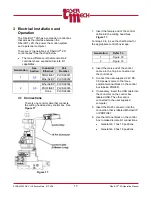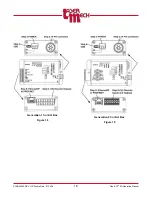
PLMNL0232 REV. H Effective Date: 01/14/19
22
FiberCUT
®
2D Operation Manual
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
V
o
lt
s
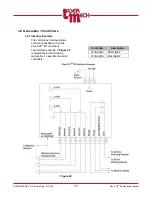
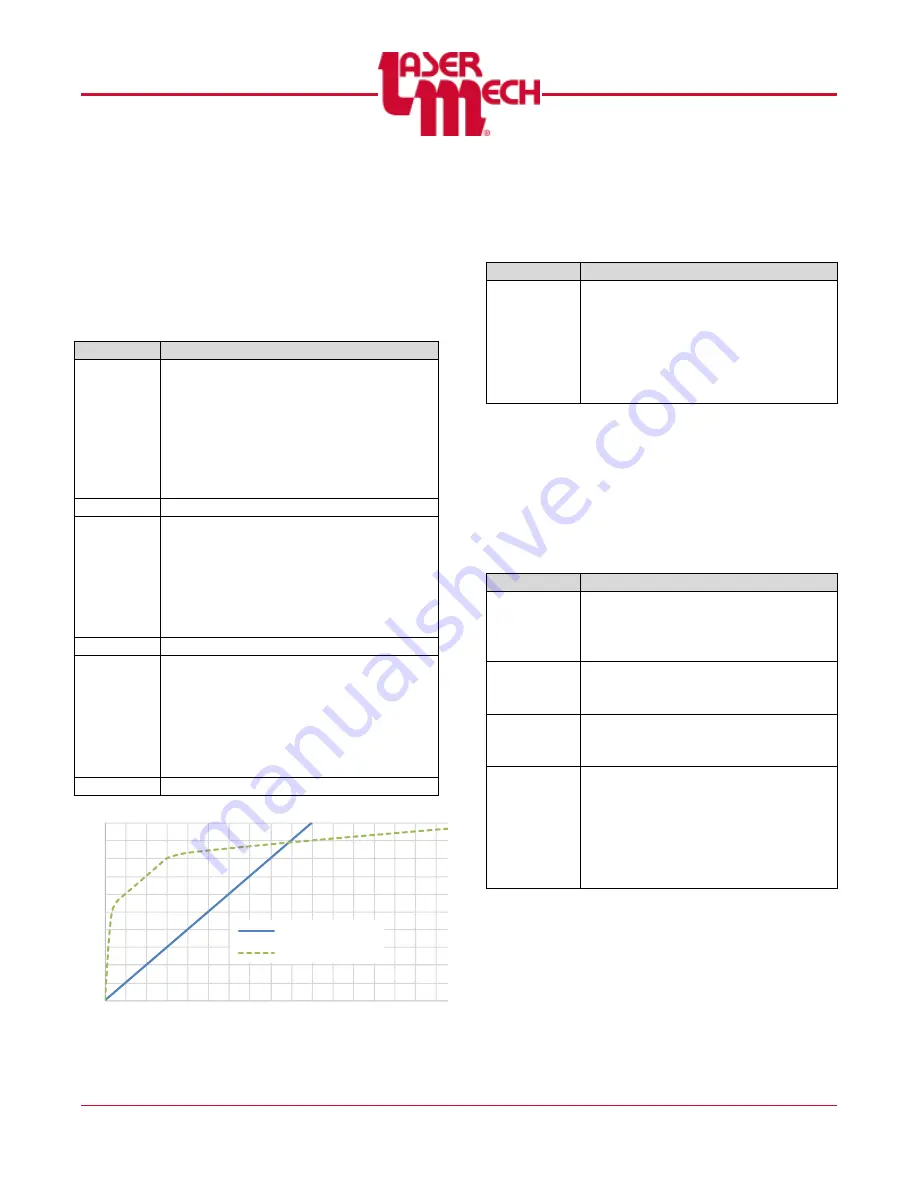
Tip Standoff Distance (mm)
HSU Output
HSU out (Linear)
HSU out (Optimized)
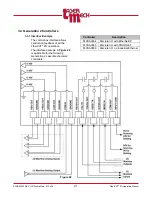
3.3.2 Terminal Block Connections
There are 3 analog outputs
(HSU, Aux and Process)
available through the terminal
block connection.
Each analog output signal is
referenced to Ground.
ANALOG OUTPUTS
OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
HSU Out
See
The HSU output signal (0-10V)
indicates the standoff distance of the
tip and the part.
In general two types of outputs
available; linear and optimized.
Additional output curves may be added
to accommodate customer
requirements.
GND
Analog Ground
Aux Out*
The Auxiliary Output is a user-defined
signal (0-10V) set using FiberCUT
®
2D
Monitor or the Industrial Ethernet
interface.
~ This output is scaled linearly from 0
to 30mm, 500mbar, or 100°C
depending on the assigned function.
GND
Analog Ground
Proc Out
The Process Monitor signal (0-10V)
indicates the status of the laser cutting
process.
~ Interpretation requires significant
processing with the user’s machine to
determine pierce through and loss of
cut values.
GND
Analog Ground
Figure 23
There is one analog input
(Lens In) available through the
terminal block.
ANALOG INPUT
INPUT
DESCRIPTION
Lens In
The Lens In signal (0-10V) is used
to specify the target position of the
lens.
The input is scaled linearly from 0-
30mm from the Home position.
Actual travel is limited to
27.5 mm.
There are 3 digital outputs
(Ready, Touch and In Pos)
available through the terminal
block connection.
Each of these outputs is a
solid-state relay connected
to Out Com when active.
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
OUTPUT
DESCRIPTION
Ready
The Ready output indicates that the
head is communicating, lens is in
position and HSU is operating with
no fault conditions.
Touch
The Touch output indicates that the
tip has contacted the part or
another conductive surface.
In Pos
The In Position output indicates that
the lens has reached the
commanded position.
Out Com
The Output Common allows the
user to configure the outputs for
sourcing or sinking.
~ Connect Out Com to 24 V DC for
“sourcing.”
~ Connect Out Com to 0 V DC for
“sinking.”