KGC-1
Chapter 1
Operation Manual
General
Chapter 1 General
1.1
About GPS compass
1.1.1 Principle of GPS positioning system
GPS (Global Positioning System) is a position measuring system using the artificial satellites, which
consists 27 artificial satellites (4 satellites per orbit x 6 orbits plus 3 reserve satellites), orbiting the
earth every 11hours 58 minutes along a circular path above the earth. In this system, positioning of a
point on the earth is achieved utilizing the triad system that a position on the earth is computed from
the distances from 3 satellites. The intersection of 3 imaginary arcs developed from each satellite
gives the own position (longitude, altitude and altitude) on the surface.
1.1.2 How the GPS Compass works?
In GPS positioning system, own position is obtained by analyzing the CA code sent from the satellites,
to compute the distance from the satellites to the user. In contrast, the GPS Compass utilizes the radio
wave itself that carries the positional data.
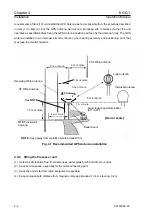
The GPS Compass uses two GPS antennas for reception. Knowing the time difference of the radio
wave arrival at each antenna, positional arrangement with respect to the satellite as well as the angle
of the incoming radio wave are computed. From the information sent from the satellite, the satellite
position is obtained. As a result, the direction of the two GPS antenna against north can be computed.
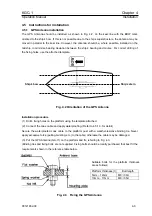
To obtain a correct ship’s heading the GPS Compass unit should sited somewhere on the line that
connects across the ship’s bow and stern
,
Fig. 1.1
Principle of the measurement by the GPS Compass
θ:
Angle of arrival of the GPS
radio wave
θ
Time difference of radio wave arrival
Ship’s bow
Heading direction
θ
93121652-01
1-1