KOBIL Smart Card Terminal Manual
Page
40
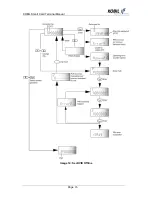
9.2 Directories
Directories are special files the system needs in order to be able to manage and
structure the data. They contain directory entries describing the files and sub
directories they contain. A directory entry consists of five bytes, and has the following
structure:
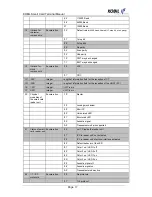
Byte Significance
Coding
1 - 2
ID
16 Bit binary
3
Displays (flags)
Bit 1 (LSB) File is stored in the ROM
Bit 2
File is stored in the RAM
Bit 3
0 (reserved)
Bit 4
0 (reserved)
Bit 5
0 (reserved)
Bit 6
0 (reserved)
Bit 7
0 (reserved)
Bit 8
(MSB)
0 (reserved)
4 - 5
Internal use
16 Bit binary (pointer)
Table 12: Coding the Directory Entries
The first entry of a given directory refers to the super-ordinate directory (parent). At
the root of the file system – which is the master file – the master file itself serves as
super-ordinate directory. Directories can be read like normal files, but not be
inscribed by the user. At any time, the file system has an active directory that the
command ‘Select File’ causes to be searched. If a file that is a directory is selected
under ‘Select File’-command, the file becomes the active directory. A reset will set
the master file to be the active directory.