501054-UIM-A-0909
4
Johnson Controls Unitary Products
PRECAUTIONS DURING LINE INSTALLATION
1.
Install the lines with as few bends as possible. Care must be taken
not to damage the couplings or kink the tubing. Use clean hard
drawn copper tubing where no appreciable amount of bending
around obstruction is necessary. If soft copper must be used, care
must be taken to avoid sharp bends which may cause a restriction.
2.
The lines should be installed so that they will not obstruct service
access to the coil, air handling system or filter.
3.
Care must also be taken to isolate the refrigerant lines to minimize
noise transmission from the equipment to the structure.
4.
The vapor line must be insulated with a minimum of 1/2" foam rub-
ber insulation (Armaflex or equivalent). Liquid lines that will be
exposed to direct sunlight and/or high temperatures must also be
insulated.
Tape and suspend the refrigerant lines as shown. DO NOT allow tube
metal-to-metal contact. See Figure 2.
5.
Use PVC piping as a conduit for all underground installations as
shown in Figure 3. Buried lines should be kept as short as possible
to minimize the build up of liquid refrigerant in the vapor line during
long periods of shutdown
6.
Pack fiberglass insulation and a sealing material such as perma-
gum around refrigerant lines where they penetrate a wall to reduce
vibration and to retain some flexibility.
7.
See Form 690.01-AD1V for additional piping information.
PRECAUTIONS DURING BRAZING OF LINES
All outdoor unit and evaporator coil connections are copper-to-copper
and should be brazed with a phosphorous-copper alloy material such
as Silfos-5 or equivalent. DO NOT use soft solder. The outdoor units
have reusable service valves on both the liquid and vapor connections.
The total system refrigerant charge is retained within the outdoor unit
during shipping and installation. The reusable service valves are pro-
vided to evacuate and charge per this instruction.
Serious service problems can be avoided by taking adequate precau-
tions to assure an internally clean and dry system.
PRECAUTIONS DURING BRAZING SERVICE VALVE
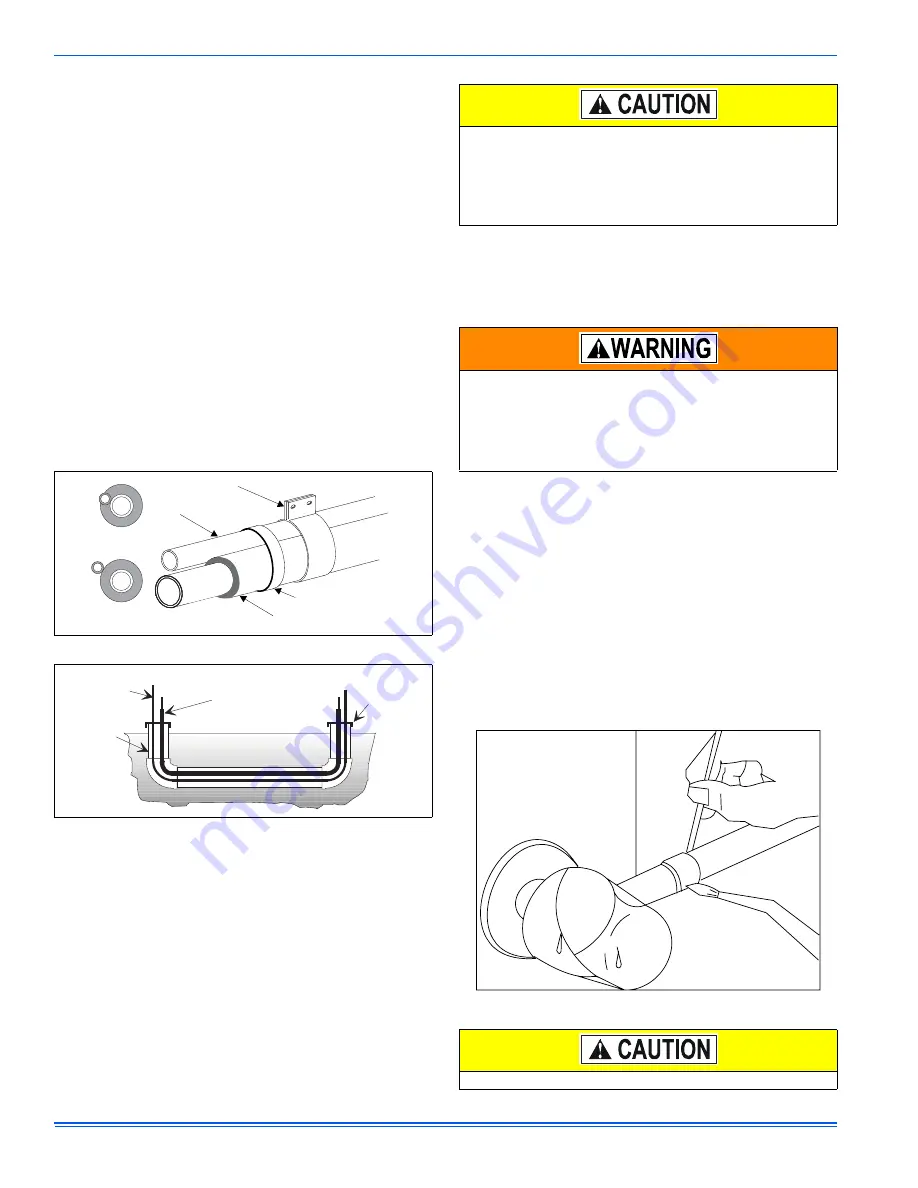
Precautions should be taken to prevent heat damage to service valve
by wrapping a wet rag around it as shown in Figure 4. Also, protect all
painted surfaces, insulation, and plastic base during brazing. After braz-
ing cool joint with wet rag.
Valve can be opened by removing the plunger cap and fully inserting a
hex wrench into the stem and backing out counter-clockwise until valve
stem just touches the chamfered retaining wall.
Connect the refrigerant lines using the following procedure:
1.
Remove the cap and Schrader core from both the liquid and vapor
service valve service ports at the outdoor unit. Connect low pres-
sure nitrogen to the liquid line service port.
2.
Braze the liquid line to the liquid valve at the outdoor unit. Be sure
to wrap the valve body with a wet rag. Allow the nitrogen to con-
tinue flowing. Refer to the Tabular Data Sheet for proper liquid line
sizing.
3.
Carefully remove the rubber plugs from the evaporator liquid and
vapor connections at the indoor coil.
4.
Braze the liquid line to the evaporator liquid connection. Nitrogen
should be flowing through the evaporator coil.
FIGURE 2:
Tubing Hanger
FIGURE 3:
Underground Installation
Liquid
Line
Incorrect
Correct
Tape
Sheet Metal Hanger
Insulated Vapor Line
TO INDOOR COIL
TO O UTDOOR UNIT
LIQUID LINE
CAP
PVC
CONDUIT
INSULATED
VAPOR LINE
Dry nitrogen should always be supplied through the tubing while it
is being brazed, because the temperature required is high enough
to cause oxidation of the copper unless an inert atmosphere is pro-
vided. The flow of dry nitrogen should continue until the joint has
cooled. Always use a pressure regulator and safety valve to insure
that only low pressure dry nitrogen is introduced into the tubing.
Only a small flow is necessary to displace air and prevent oxidation.
This is not a backseating valve. The service access port has a
valve core. Opening or closing valve does not close service access
port.
If the valve stem is backed out past the chamfered retaining wall,
the O-ring can be damaged causing leakage or system pressure
could force the valve stem out of the valve body possibly causing
personal injury.
FIGURE 4:
Heat Protection
The evaporator is pressurized.
















