Installation
ANCA Motion
D-000168 Rev 02
33
6
Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC)
6.3.3
While the ultimate responsibility for a system’s EMC compliance lies with the system builder, the LinX motor’s
design provides good EMC performance as a system component. The aluminum forcer housing that contains the
motor windings effectively limits both radiated noise emission from the motor during operation and external
sources of noise from impacting connected electronics.
The following are general recommendations when using the LinX motor to minimize Electromagnetic Interference
(EMI) in the system.
Keep all cable routing as short and direct as possible.
Separate low voltage signal cables from power cables and noisy components.
Ensure cable shielding is terminated correctly.
Other sources of EMI in the system, such as servo drives, must also be considered for EMC, refer to component
documentation for further information.
Servo Drive Configuration
6.4
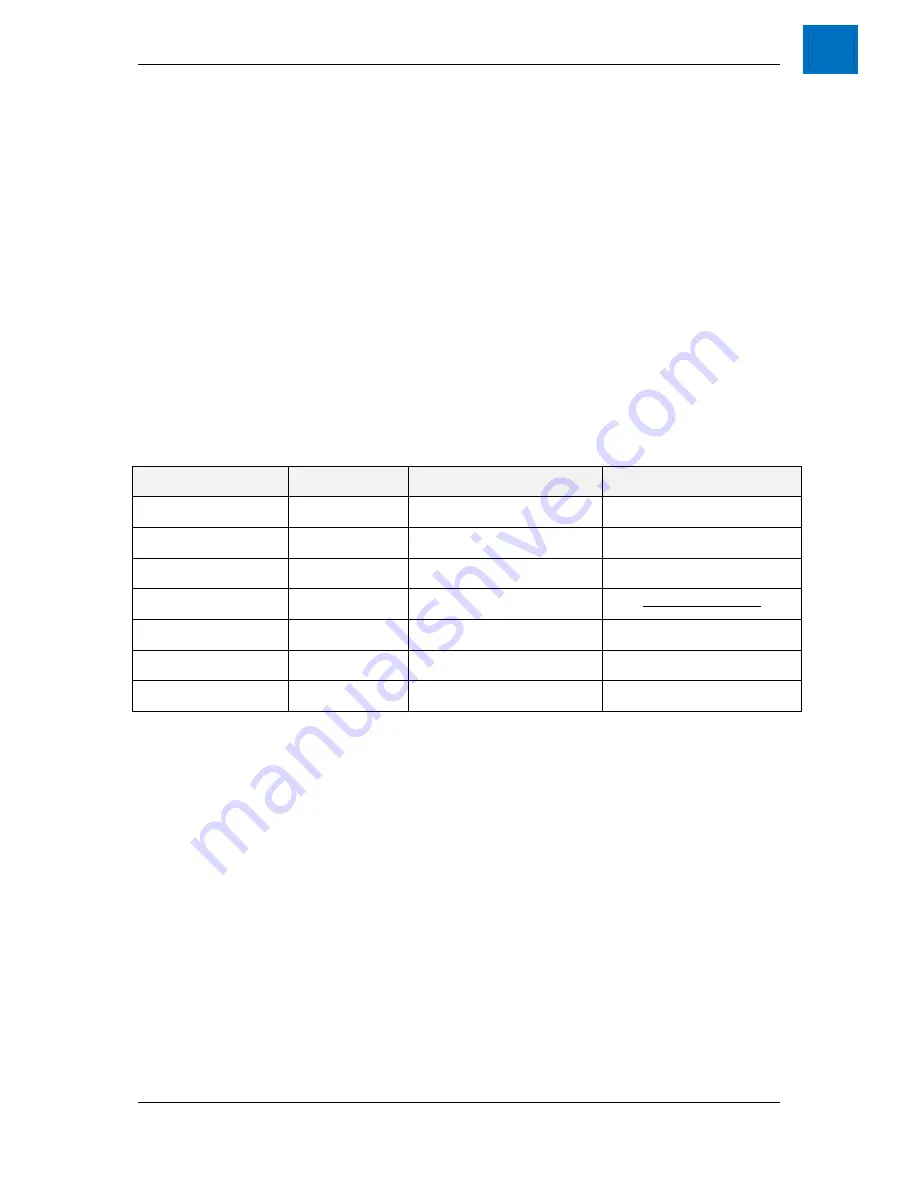
In general, servo drives will need the following configuration to control the LinX motor. Servo drives that do not
specifically support linear motors can be configured as a two pole rotary motor. Configuration requirements will
depend on the specific servo drive and linear encoder used; refer to product documentation for specific
information.
Parameter
Units
Linear Motor
Linear as Rotary Motor
Motor Type
-
Linear
Rotary
Distance between
magnet poles
Distance or
encoder counts
As per motor specification
As per motor specification
Number of Motor Poles
Integer
-
2
Rotary encoder pulses
per revolution
Encoder
counts/lines
-
Magnet itch
Linear Encoder itch
Linear encoder pitch
Distance
As per encoder specification
-
Peak Current
Amps
As per motor specification
As per motor specification
Continuous Current
Amps
As per motor specification
As per motor specification
Table 6-1 - Servo drive configuration






































