Operation
Before starting any welding activity ensure that you have
suitable eye protection and protective clothing. Also take
the necessary steps to protect any persons within the
area.
MMA
After connecting the welding leads as detailed you will need
to switch on the machine. The power LED will be lit and the
fan running.
Switch the MMA/MIG switch to MMA.
Set the amperage on the machine using the MMA current
control knob to a value suitable for the electrode being used.
Please see below a guide to amperages required. Ensure
you check that you have the electrode polarity correct.
Inductance can be adjusted using the inductance control on
the front panel of the machine
MIG/MAG
1)
After being installed as above, and the power switch
on the back panel being switched on, the machine is started.
At this time, the ammeter displays the preset wire feed
speed value, and the voltmeter displays the preset voltage
value. Open the cylinder valve, and switch the gas check
switch to the “GAS CHECK” position. Adjust the gas
regulator to get the correct gas flow. After setting, switch the
gas check switch to the “Welding” position.
2)
Get the correct arc conditions by adjusting the
inductance control knob. Turn the knob counterclockwise to
get lower inductance and harder arc; turn it clockwise to get
higher inductance and softer arc. Generally, select harder arc
at lower current, while select softer arc at higher currents.
3)
Select the correct welding current and welding
voltage by adjusting the current control knob and voltage
control knob on the wire feeder.
4
Select 2T or 4T operation mode. In 2T mode, the arc
is ignited by pushing the torch trigger, and arc stops by
releasing the torch trigger. In 4T mode, welding can be
continued when releasing the torch trigger after arc is
ignited, and at this time, welding instructions should be set
by adjusting the current control knob and voltage control
knob on the wire feeder. When pushing the torch trigger
again, the machine enters into crater welding, and at this
time. Crater parameters should be set by adjusting the
crater/welding current control knob and crater voltage
control knob on the front panel of the machine.
The actual current and voltage values are displayed on the
front panel of the machine. When the torch trigger is
released, welding ends. 2 seconds after welding ends, the
gas supply will be cut o
ff
.
Gas selection
Metal inert gas welding (MIG): Uses Argon (Ar), Helium (He)
or Ar-He mixtures as the shield gas, and it mainly used for
welding aluminium and its alloys.
Metal active gas welding (MAG): Uses Argon (Ar) mixed with
a certain amount of CO
2
/ O
2
as the shield gas, and it usually
used in short circuit transfer and spray transfer. It can be
applicable to flat position welding, vertical position welding,
overhead position welding and all-position welding, and it
mainly used for welding carbon steel, high strength low alloy
steel and stainless steel. Welding robots mostly use the
MAG process.
CO2 (carbon dioxide) gas shielded arc welding (CO2
welding): It uses CO2 as the shield gas, and is usually used
in globular transfer and short circuit transfer to implement
welding. It can be used to weld in di
ff
erent positions. As
compared with other welding methods, CO2 welding has
many advantages, though it produces more spatters, CO2
welding is widely used for general metal structure welding.
1) Welding current setting
Set the welding current after the above preparation. Short
circuit transfer is mainly for electrode wires of diameter
0.6~1.2mm. As a guide for short circuit welding set the
welding current according to the table below.
2) Welding speed selection
The welding quality and productivity should be taken into
consideration for the selecting of welding speed. In the case
that the welding speed increases, it weakens the protection
11
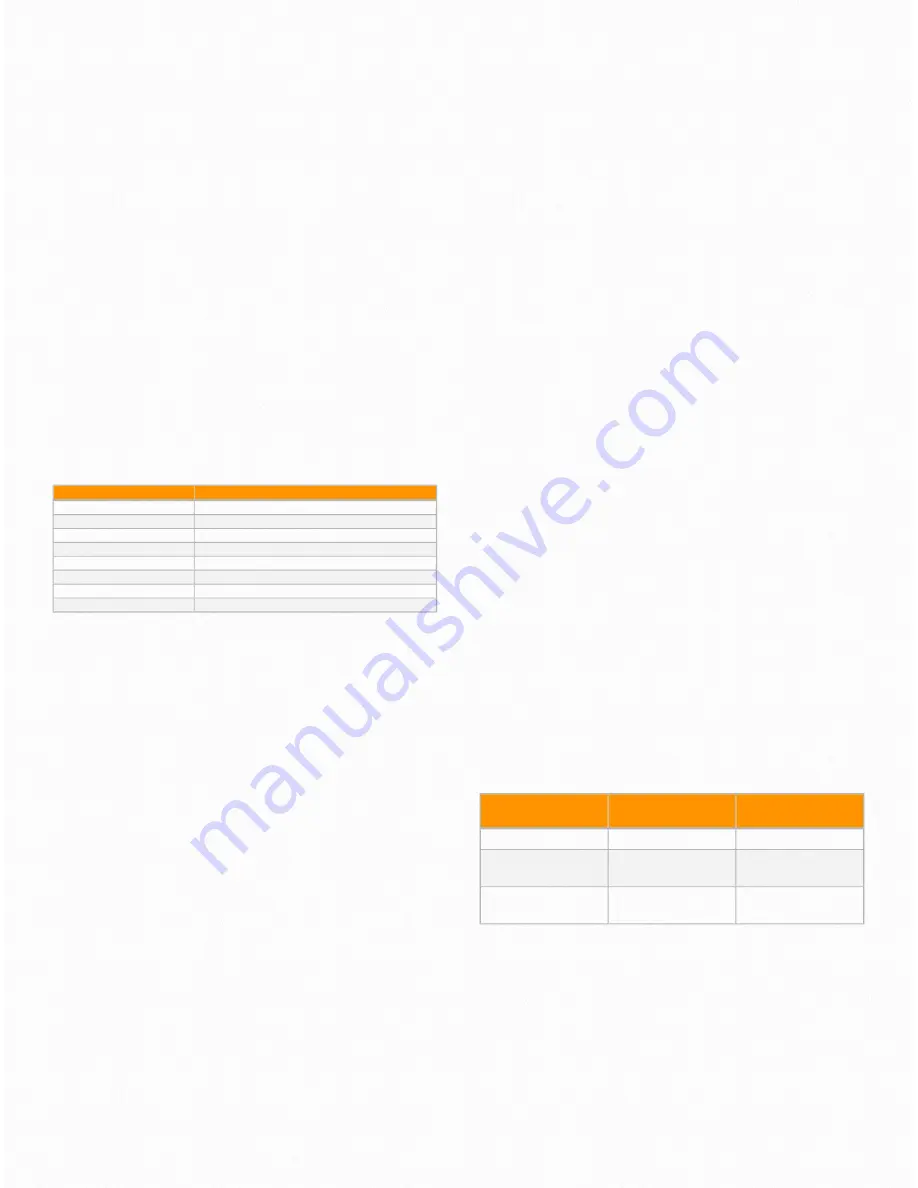
Electrode Diameter (mm)
Recommended Welding Current (A)
1.0
20~60
1.6
44~84
2.0
60~100
2.5
80~120
3.2
108~148
4.0
140~180
5.0
180~220
6.0
220~260
Welding wire
φ
(mm)
Applicable current (A)
Optimal current (A)
0.8
50~120
70~100
1.0
70~180
80~120
1.2
80~350
100~200
Summary of Contents for JM-250S MIG Series
Page 16: ...Electrical schematic 7 15 ...
Page 17: ...Parts list 8 16 ...






































