10
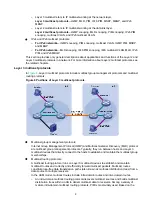
forwarding mechanism, PIM has dense mode (often referred to as "PIM-DM") and sparse
mode (often referred to as "PIM-SM").
{
An inter-domain multicast routing protocol is used for delivering multicast information
between two ASs. So far, mature solutions include Multicast Source Discovery Protocol
(MSDP) and MBGP. MSDP propagates multicast source information among different ASs.
MBGP is an extension of the MP-BGP for exchanging multicast routing information among
different ASs.
For the SSM model, multicast routes are not divided into intra-domain routes and inter-domain
routes. Because receivers know the position of the multicast source, channels established
through PIM-SM are sufficient for the transport of multicast information.
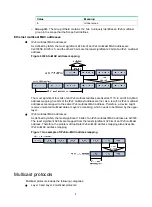
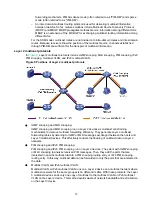
Layer 2 multicast protocols
, Layer 2 multicast protocols include IGMP snooping, MLD snooping, PIM snooping, IPv6
PIM snooping, multicast VLAN, and IPv6 multicast VLAN.
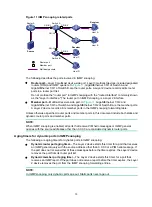
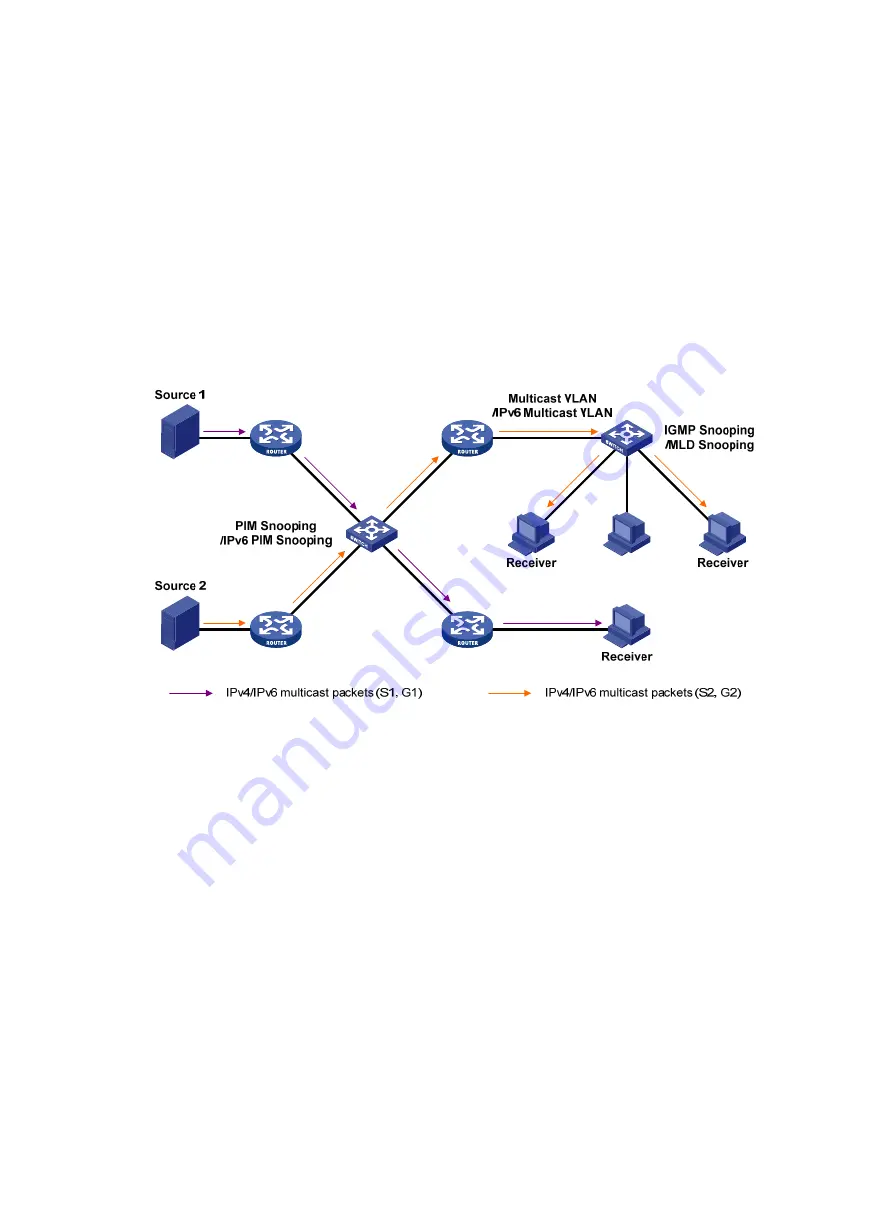
Figure 9 Positions of Layer 2 multicast protocols
•
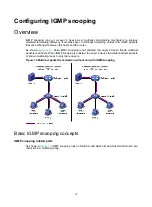
IGMP snooping and MLD snooping:
IGMP snooping and MLD snooping run on Layer 2 devices as multicast constraining
mechanisms to improve multicast forwarding efficiency. They generate Layer 2 multicast
forwarding tables by listening to IGMP or MLD messages exchanged between the hosts and
Layer 3 multicast devices. This effectively controls the flooding of multicast data in Layer 2
networks.
•
PIM snooping and IPv6 PIM snooping:
PIM snooping and IPv6 PIM snooping run on Layer 2 devices. They work with IGMP snooping
or MLD snooping to analyze received PIM messages. Then, they add the ports that are
interested in specific multicast data to a PIM snooping routing entry or IPv6 PIM snooping
routing entry. In this way, multicast data can be forwarded to only the ports that are interested in
the data.
•
Multicast VLAN and IPv6 multicast VLAN:
Multicast VLAN or IPv6 multicast VLAN runs on a Layer 2 device on a multicast network where
multicast receivers for the same group exist in different VLANs. With these protocols, the Layer
3 multicast device sends only one copy of multicast to the multicast VLAN or IPv6 multicast
VLAN on the Layer 2 device. This method avoids waste of network bandwidth and extra burden
on the Layer 3 device.