1 Your PC’s Performance Features
Matching Memory Capacity to Your Requirements
18
English
What Else is Memory
Used For?
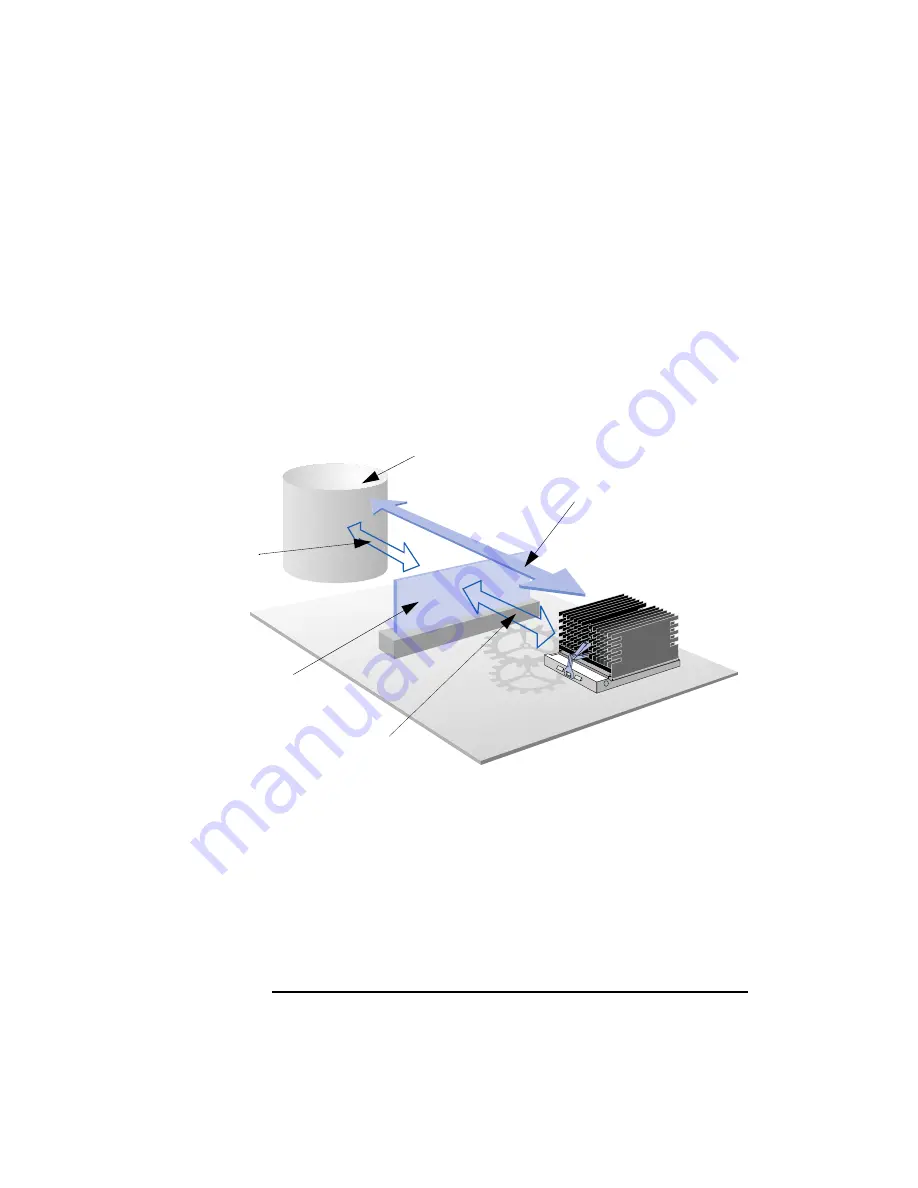
Many operating systems use memory to accelerate data transfers with
the PC’s hard disks. To do this, an area of memory is dedicated to a disk
cache, which stores copies of the latest data read from or written to the
hard disks. If the processor then accesses the same data again, it will be
loaded from memory at much higher speed than from hard disk.
Because much of your PC’s work is repetitive, disk caches offer a
significant performance advantage with most applications. The amount
of memory dedicated to the disk cache is determined by the operating
system you are using.
Some operating systems, such as Windows for Workgroups, allocate a
fixed disk cache, which you can configure directly. Others, such as
Windows NT and Windows 95, use a dynamic allocation mechanism
that configures the disk cache according to the amount of memory
available.
The memory used by the disk cache will not be available for use by
your applications. When determining your memory requirement,
remember to add an extra allowance for the disk cache.
Hard disk drive
Memory dedicated
to the disk cache
Data accessed at
the access speed of
the hard disk drive
(typically 10 mS)
Data copied from
the hard disk drive
to the disk cache
Data accessed at the
access speed of
memory (60 nS)
















































