76
Authentication procedure
The 802.1X authentication procedure varies with the way the network access device handles EAP
messages.
EAP relay
EAP relay is defined in IEEE 802.1X. In this mode, EAP packets are carried in an upper layer protocol
such as RADIUS so that they can go through complex networks to reach the authentication server. EAP
relay requires that the RADIUS server support the EAP-Message and Message-Authenticator attributes.
shows the EAP packet exchange procedure with EAP-MD5.
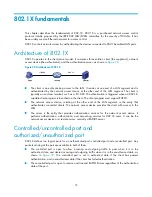
Figure 34
802.1X authentication procedure in EAP relay mode
EAPOL
EAPOR
(1) EAPOL-Start
(2) EAP-Request/Identity
(3) EAP-Response/Identity
(6) EAP-Request/MD5 challenge
(10) EAP-Success
(7) EAP-Response/MD5 challenge
(4) RADIUS Access-Request
(EAP-Response/Identity)
(5) RADIUS Access-Challenge
(EAP-Request/MD5 challenge)
(9) RADIUS Access-Accept
(EAP-Success)
(8) RADIUS Access-Request
(EAP-Response/MD5 challenge)
(11) Handshake request
(EAP-Request/Identity )
(13) EAPOL-Logoff
......
Client
Device
Server
Port authorized
Handshake timer
Port unauthorized
(12) Handshake response
(EAP-Response/Identity )
1.
When a user launches the 802.1X client software and enters a registered username and password,
the 802.1X client software generates an EAPOL-Start packet and sends it to the device to initiate an
authentication process.
2.
Upon receiving the EAPOL-Start packet, the device responds with an EAP-Request/Identity packet
for the username of the client.