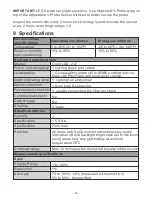
Prolonged and/or excessive patient movement
Intravascular dyes or externally applied coloring, such as nail polish
or pigmented cream
failure to cover the sensor site with opaque material in high ambient
light conditions
Loss-of-pulse signal can occur for the following reasons:
The sensor is applied too tightly
A blood pressure cuff is inflated on the same extremity as the one
with the sensor attached
There is arterial occlusion proximal to the sensor
Poor peripheral perfusion
5.5 Alarms
Alarms triggered by a vital sign that appears abnormal or by technical problems
of the Pulse Oximeter, are presented to the user by visual and audible alarm
indications.
By nature, the pulse oximeter's alarms can be classified into three
categories: physiological alarms, technical alarms and prompt messages.
1) Physiological alarms
Physiological alarms, also called patient status alarm, are triggered
by a monitored parameter value that violates set alarm limits or an
abnormal patient condition.
2) Technical alarms
Technical alarms, also called system status alarms, are triggered by
a device malfunction or a patient data distortion due to improper
operation or system problems.
3) Prompt messages
In fact, prompt messages are not alarm messages, which are
displayed in the technical alarm area. Apart from the physiological
and technical messages, the pulse oximeter will show some
messages which indicate the system status.
5.5.1 Alarm Categories
By severity, the pulse oximeter's physiological alarms can be classified
into three categories: high level alarms, medium level alarms and low
level alarms.
1) High level alarms
Indicate that the patient is in a life threatening situation and an
emergency treatment is demanded.
5.5.2 Alarm Levels
2) Medium level alarms
Indicate that the patient's vital signs appear abnormal and an
immediate treatment is required.
-17-