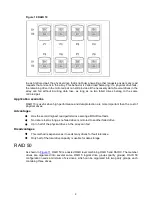
2
Figure 2 The read/write heads of all the constituent physical drives are active
simultaneously
Data striping
Data striping divides continuous data into parts of the same size and writes these parts into different
drives. As shown in
, each unit of data is called a block (denoted by B
n
), and adjacent
blocks form a set of data stripes (S
n
) across all the physical drives that comprise the logical drive.
Because the read/write heads are active simultaneously, the same amount of data is written to each
drive during any given time interval.
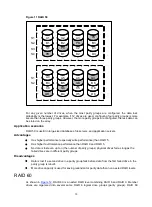
Figure 3 Data blocks and stripes
For data in the logical drive to be readable, the data block sequence must be the same in every
stripe. This sequencing process is performed by the storage controller, which sends the data blocks
to the drive write heads in the correct order.
Summary of Contents for UniServer E3200 G3
Page 35: ...19 Figure 29 Selecting the RAID volume to be deleted...
Page 116: ...56 Figure 96 Controller Configuration screen...
Page 220: ...61 Figure 109 Selecting Main Menu 2 Select Controller Management and press Enter...
Page 243: ...84 Figure 153 Confirming the operation...
Page 293: ...50 Figure 89 Clearing completion...
Page 382: ...21 Figure 27 Storage controller information...
Page 389: ...7 Figure 8 Identifying a storage controller 2...