11
•
Alternate
port
—Acts as the backup port for a root port. When the root port is blocked, the
alternate port takes over.
•
Backup
port
—Acts as the backup port of a designated port. When the designated port is
invalid, the backup port becomes the new designated port. A loop occurs when two ports of the
same spanning tree device are connected, so the device blocks one of the ports. The blocked
port is the backup port.
•
Edge
port
—Directly connects to a user host rather than a network device or network segment.
Port states
RSTP uses the discarding state to replace the disabled, blocking, and listening states in STP.
shows the differences between the port states in RSTP and STP.
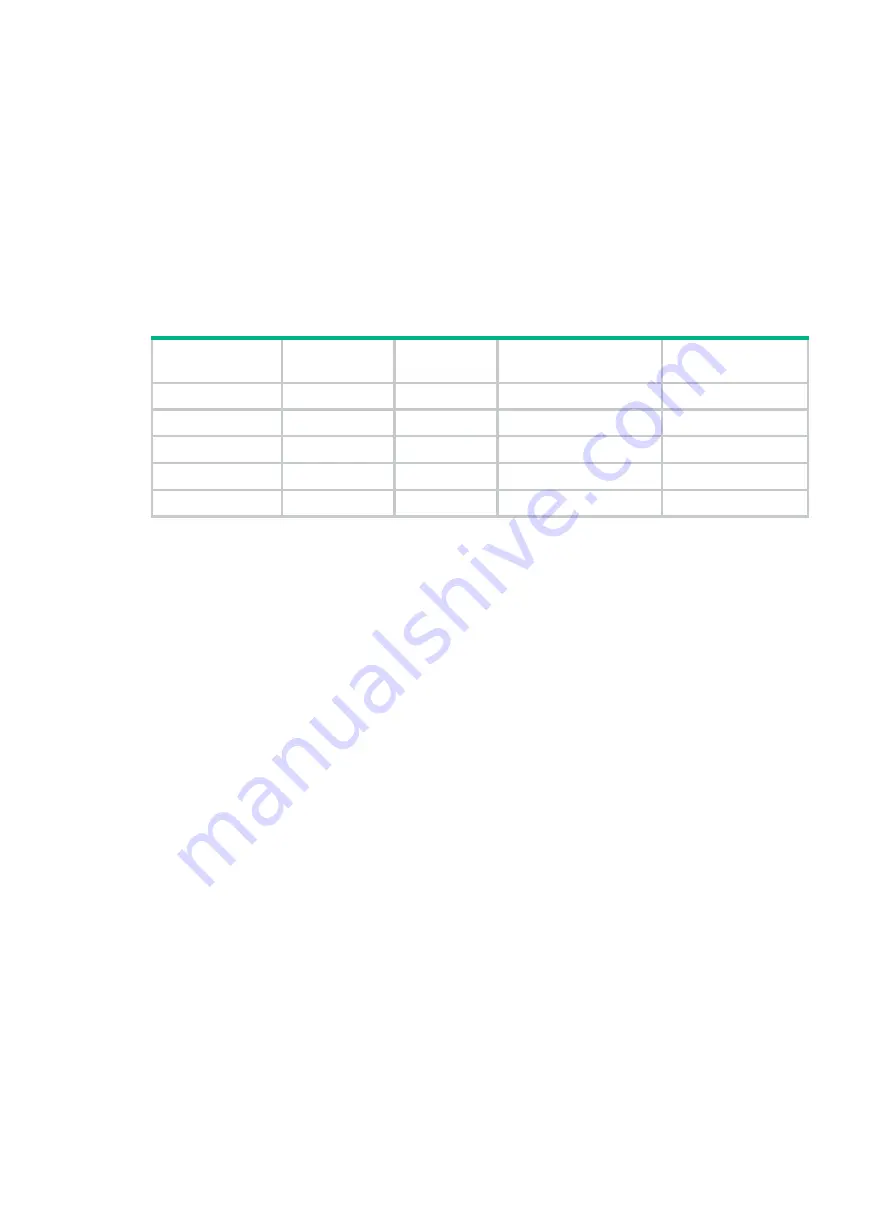
Table 5 Port state differences between RSTP and STP
STP port state
RSTP port
state
Sends
BPDU
Learns MAC
addresses
Forwards user
data
Disabled Discarding
No No
No
Blocking Discarding
No No
No
Listening Discarding
Yes No
No
Learning Learning
Yes Yes
No
Forwarding Forwarding
Yes
Yes
Yes
How RSTP works
During RSTP calculation, the following events occur:
•
If a port in discarding state becomes an alternate port, it retains its state.
•
If a port in discarding state is elected as the root port or designated port, it enters the learning
state after the forward delay. The port learns MAC addresses, and enters the forwarding state
after another forward delay.
{
A newly elected RSTP root port rapidly enters the forwarding state if the following
requirements are met:
−
The old root port on the device has stopped forwarding data.
−
The upstream designated port has started forwarding data.
{
A newly elected RSTP designated port rapidly enters the forwarding state if one of the
following requirements is met:
−
The designated port is configured as an edge port which directly connects to a user
terminal.
−
The designated port connects to a point-to-point link and receives a handshake
response from the directly connected device.
RSTP BPDU processing
In RSTP, a non-root bridge actively sends RSTP BPDUs at the hello time through designated ports
without waiting for the root bridge to send RSTP BPDUs. This enables RSTP to quickly detect link
failures. If a device fails to receive any RSTP BPDUs on a port within triple the hello time, the device
considers that a link failure has occurred. After the stored configuration BPDU expires, the device
floods RSTP BPDUs with the TC flag set to initiate a new RSTP calculation.
In RSTP, a port in blocking state can immediately respond to an RSTP BPDU with a lower priority
than its own BPDU.
Summary of Contents for S6850 Series
Page 108: ...48 WGE1 0 3 32768 49153 50100 0x7b 0001 0001 0001 ACDEF...
Page 259: ...21 6 N A 200 6...
Page 337: ...ii...
















































