166
contains a null MAC address TLV list, these PEs remove all MAC addresses from the specified VSI,
except for those learned from the PW that sent the message.
•
MAC address aging
Remote MAC addresses learned by a PE that are related to VC labels but no longer in use must be
aged out by an aging mechanism. The aging mechanism used here is the aging timer
corresponding to the MAC address. When receiving a packet whose source MAC address has an
aging timer started, the PE resets the aging timer.
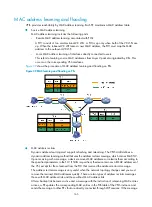
VPLS loop avoidance
To avoid loops in a VPLS network, full mesh and split horizon forwarding are used instead of STP at the
private network side.
•
Full mesh
—PEs are logically fully meshed (as are the PWs). Each PE must create for each VPLS
forwarding instance a tree to all other PEs of the instance.
•
Split horizon forwarding
—Each PE must support horizontal split to avoid loops. A PE cannot
forward packets through PWs of the same VSI, because all PEs of a VSI are directly connected.
Packets from PWs on the public network side cannot be forwarded to other PWs. They can only be
forwarded to the private network side.
VPLS packet encapsulation
This section describes VPLS packet encapsulation.
Packet encapsulation on an AC
The packet encapsulation type of an AC depends on the user VSI access mode, which can be VLAN or
Ethernet.
•
VLAN access
—The Ethernet header of a packet sent by a CE to a PE or sent by a PE to a CE includes
a VLAN tag that is added in the header as a service delimiter for the service provider network to
identify the user. The tag is called a "P-Tag."
•
Ethernet access
—The Ethernet header of a packet upstream from the CE or downstream from the PE
does not contain any service delimiter. If a header contains a VLAN tag, it is the internal VLAN tag
of the user and means nothing to the PE. This kind of internal VLAN tag of the user is called a
"U-Tag."
You can specify the VSI access mode to be used.
Packet encapsulation on a PW
The packet encapsulation type of a PW, also called the "PW transport mode," can be either Ethernet or
VLAN.
•
In Ethernet mode, P-Tag is not transferred on the PW. For a packet from a CE, if it contains the
service delimiter, the PE removes the service delimiter and adds a PW label and a tunnel label into
the packet before forwarding the packet. Otherwise, the PE adds a PW label and a tunnel label into
the packet and then forwards the packet. For a packet to be sent downstream, whether the PE adds
the service delimiter into the packet depends on your configuration. However, rewriting and
removing the existing tags are not allowed.
•
In VLAN mode, packets transmitted over the PW must carry a P-Tag. For a packet from a CE, if it
contains the service delimiter, the PE keeps the P-Tag unchanged or changes the P-Tag to the VLAN
tag expected by the peer PE or to a null tag (the tag value is 0), and then adds a PW label and a
tunnel label into the packet before sending the packet out. If the packet contains no service delimiter,